Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A block of mass 1 kg is placed at point A of a rough track shown in figure following. If slightly pushed towards right, it stops at point B of the track. Calculate the work done by the frictional force on the block during its transit from A to B.

उत्तर
\[\text{ Given }, \]
\[\text{ Mass of the block, m = 1 kg }\]
\[\text{ Height of point A, H = 1 m }\]
\[\text{ Height of point B, h = 0 . 8 m }\]
Work done by friction = Change in potential energy of the body
\[\Rightarrow \text{W}_1 = \text{ mgh - mgH}\]
\[ = 1 \times 10 \left( 0 . 8 - 1 \right)\]
\[ = - 1 \times 10 \times \left( 0 . 2 \right) = - 2 \text{ J } \]
The work done by the frictional force on the block during its transit from A to B is - 2 joule.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State if the following statement is true or false. Give a reason for your answer.
Work done in the motion of a body over a closed loop is zero for every force in nature.
When you hold a pen and write on your notebook, what kind of force is exerted by you on the pen? By the pen on the notebook? By you on the notebook?
Is it true that the reaction of a gravitational force is always gravitational, of an electromagnetic force is always electromagnetic and so on?
If all matters were made of electrically neutral particles such as neutrons,
(a) there would be no force of friction
(b) there would be no tension in the string
(c) it would not be possible to sit on a chair
(d) the earth could not move around the sun.
The gravitational force acting on a particle of 1 g due to a similar particle is equal to 6.67 × 10−17 N. Calculate the separation between the particles.
A body builder exerts a force of 150 N against a bullworker and compresses it by 20 cm. Calculate the spring constant of the spring in the bullworker.
A satellite is projected vertically upwards from an earth station. At what height above the earth's surface will the force on the satellite due to the earth be reduced to half its value at the earth station? (Radius of the earth is 6400 km.)
A small block of mass m is kept on a rough inclined surface of inclination θ fixed in an elevator. the elevator goes up with a uniform velocity v and the block does not slide on the wedge. The work done by the force of friction on the block in time t will be
A block of mass m slides down a smooth vertical circular track. During the motion, the block is in
A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the plane. The motion of the particle takes place in a plane. It follows that
(a) its velocity is constant
(b) its acceleration is constant
(c) its kinetic energy is constant
(d) it moves in a circular path.
No work is done by a force on an object if
(a) the force is always perpendicular to its velocity
(b) the force is always perpendicular to its acceleration
(c) the object is stationary but the point of application of the force moves on the object
(d) the object moves in such a way that the point of application of the force remains fixed.
A man moves on a straight horizontal road with a block of mass 2 kg in his hand. If he covers a distance of 40 m with an acceleration of 0⋅5 m/s2, find the work done by the man on the block during the motion.
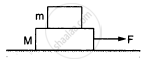
A block of mass m is kept over another block of mass M and the system rests on a horizontal surface (In the following figure). A constant horizontal force F acting on the lower block produces an acceleration \[\frac{F}{2 \left( m + M \right)}\] in the system, and the two blocks always move together. (a) Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bigger block and the horizontal surface. (b) Find the frictional force acting on the smaller block. (c) Find the work done by the force of friction on the smaller block by the bigger block during a displacement d of the system.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Find the kinetic energy of the block at the instant the force ceases to act. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A force F = 20 + 10y acts on a particle in y-direction where F is in newton and y in metre. Work done by this force to move the particle from y – 0 to y – 1 m is:
A bicyclist comes to a skidding stop in 10 m. During this process, the force on the bicycle due to the road is 200 N and is directly opposed to the motion. The work done by the cycle on the road is ______.
A body of mass 0.5 kg travels in a straight line with velocity v = a x3/2 where a = 5 m–1/2s–1. The work done by the net force during its displacement from x = 0 to x = 2 m is ______.
A body is being raised to a height h from the surface of earth. What is the sign of work done by applied force?
A body is being raised to a height h from the surface of earth. What is the sign of work done by gravitational force?
