Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Water falling from a 50-m high fall is to be used for generating electric energy. If \[1 \cdot 8 \times {10}^5 \text{ kg } \] of water falls per hour and half the gravitational potential energy can be converted into electrical energy, how many 100 W lamps can be lit with the generated energy?
उत्तर
Given :
\[\text{ Height, h = 50 m } \]
\[\text{ Mass of water falling per hour, m } = 1 . 8 \times {10}^5 \text{ kg } \]
Power of a lamp,
\[P = 100 \text{ watt } \]
\[\text{ Potential energy of the water }, \]
\[\text{ P . E . = mgh } \]
\[ = 1 . 8 \times {10}^5 \times 9 . 8 \times 50\]
\[ = 882 \times {10}^5 J\]
As only half the potential energy of water is converted into electrical energy,
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A body of mass m is placed on a table. The earth is pulling the body with a force mg. Taking this force to be the action what is the reaction?
Is it true that the reaction of a gravitational force is always gravitational, of an electromagnetic force is always electromagnetic and so on?
List all the forces acting on the block B in figure.
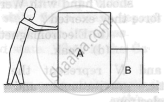
Figure shows a cart. Complete the table shown below.
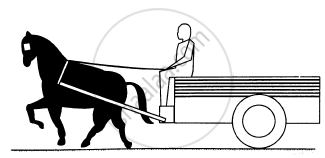
| Force on | Force by | Nature of the Force | Direction |
| Cart |
1 |
||
| Horse |
1 |
||
| Driver |
1 |
Let E, G and N represent the magnitudes of electromagnetic gravitational and nuclear forces between two electrons at a given separation. Then
A neutron exerts a force on a proton which is
(a) gravitational
(b) electromagnetic
(c) nuclear
(d) weak
A body builder exerts a force of 150 N against a bullworker and compresses it by 20 cm. Calculate the spring constant of the spring in the bullworker.
The work done by the external forces on a system equals the change in
A block of mass m slides down a smooth vertical circular track. During the motion, the block is in
A box is pushed through 4.0 m across a floor offering 100 N resistance. How much work is done by the resisting force?
A man moves on a straight horizontal road with a block of mass 2 kg in his hand. If he covers a distance of 40 m with an acceleration of 0⋅5 m/s2, find the work done by the man on the block during the motion.
A force \[F = \alpha + bx\] acts on a particle in the x-direction, where a and b are constants. Find the work done by this force during a displacement from x = 0 to x = d.
A box weighing 2000 N is to be slowly slid through 20 m on a straight track with friction coefficient 0⋅2 with the box. (a) Find the work done by the person pulling the box with a chain at an angle θ with the horizontal. (b) Find the work when the person has chosen a value of θ, which ensures him the minimum magnitude of the force.
A block of weight 100 N is slowly moved up a smooth incline of inclination 37° by a person. Calculate the work done by the person in moving the block through a distance of 2 m, if the driving force is (a) parallel to the incline and (b) in the horizontal direction.
Find the average frictional force needed to stop a car weighing 500 kg at a distance of 25 m if the initial speed is 72 km/h.
A particle of mass m moves on a straight line with its velocity varying with the distance travelled, according to the equation \[\nu = a\sqrt{x}\] , where a is a constant. Find the total work done by all the forces during a displacement from \[x = 0 \text{ to } x - d\] .
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Find the kinetic energy of the block at the instant the force ceases to act. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A body of mass 0.5 kg travels in a straight line with velocity v = a x3/2 where a = 5 m–1/2s–1. The work done by the net force during its displacement from x = 0 to x = 2 m is ______.
A body is being raised to a height h from the surface of earth. What is the sign of work done by applied force?
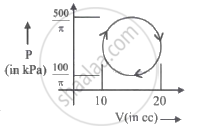
Work done by gas in cyclic process is ______ J.