Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Observe the following diagram and answer the questions.

- Explain the construction of the equipment shown in the figure.
- How is AC generated?
उत्तर
- An AC generator consists of a rotating rectangular coil ABCD placed between the two poles of a permanent magnet. The coil is attached to the two rings R1 and R2 at both ends. The two stationary conducting brushes B1 and B2 are maintained and pushed independently on the corresponding rings R1 and R2.
The coil inside the magnetic field can be rotated mechanically from the outside by turning the two internal rings R1 and R2, which are coupled to an axle. The galvanometer is linked to the two brushes' outer ends to display the direction of current flow in the specified external circuit. - According to Fleming's right-hand rule, the current is induced in these arms in the direction ABCD. After half rotation, arm CD moves down and arm AB moves up. As a result, each segment's current flow switches direction, resulting in net-induced current flowing in the direction of DCBA. As a result, the polarity of the current in each arm changes after every turn, producing an alternating current.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name some sources of direct current.
What change should be made in an a.c. generator so that it may become a d.c. generator?
State whether the following statement are true of false:
A wire with a green insulation is usually the live wire.
State whether the following statement are true of false:
A miniature circuit breaker (MCB) works on the heating effect of current.
The current induced in a closed circuit only if there is ______.
Name and state the principle of a simple a.c. generator. What is its use?
Suggest two ways in an a.c. generator to produce a higher e.m.f.
Explain the difference:
AC generator and DC generator.
The given figures 1 to 3 show the working of a simple A.C. generator. Study the diagrams and answers of the following questions.
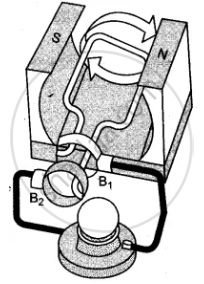
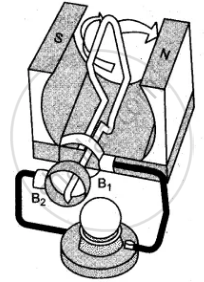
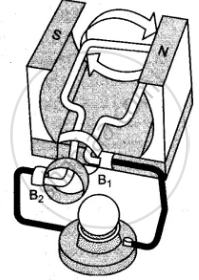
(i) State and explain the principle underlying the working of a simple generator.
(ii) Where is the loop of wire placed?
(iii) What happens when the loop is rotated?
(iv) Indicate the direction of the current flow through the wire for the first half of the turn (in first figure). Name and state the rule used in finding the direction of the current.
(v) Indicate the direction of the current for the case shown in second figure.
(vi) Indicate the direction of current in the outer circuit (i.e., electric bulb) in first and third figure.
(vii) What type of current is shown in the above diagrams? Explain.
State true or false:
The frequency of AC is 50 Hz.
A device for producing electric current is ______.
Draw and label the diagram of an AC generator.
Draw a neat diagram of an AC generator and explain its working.
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer forming a loop and a magnet is:
A: Held stationary
B: Moved away along its axis
C: Moved towards along its axis
D: There will be an induced current in
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is withdrawn from inside the coil?
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is held stationary inside the coil?
State one factor that affects the magnitude of induced current in an AC generator.
