Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Tara, after completing her exams, went to her grandmother's house along with her younger brother Rahul. One day, Rahul came home after playing and switched on the fan and air conditioner. At the same time, his grandmother was preparing a milkshake for him using a mixer. Suddenly, they heard a big sound and the electricity of the house got shut down. Tara is called an electrician. He said the main reason for supply to shut down was overloading.
- What is overloading?
- Is overloading and short the same? When does short-circuiting take place?
- How can the effects of overloading be avoided?
उत्तर
- Overloading is the term used to describe the circuit's current flow when it exceeds the allowed value.
- Short-circuiting and overloading are not the same. When a live wire and a neutral wire are in direct contact with one another, a short circuit occurs.
- Overloading can be avoided by not connecting too many appliances to the same circuit at the same time.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name any two effects of electric current.
Write Joule's law of heating.
What is nichrome? State its one use.
Give two reasons why nichrome alloy is used for making the heating elements of electrical appliances.
Why does the connecting cord of an electric heater not glow hot while the heating element does?
Write down the formula for the heat produced when a current I is passed through a resistor R for time t.
Derive the expression for the heat produced due to a current 'I' flowing for a time interval 't' through a resistor 'R' having a potential difference 'V' across its ends. With which name is this relation known?
The current passing through a room heater has been halved. What will happen to the heat produced by it?
What is meant by the heating effect of current? Give two applications of the heating effect of current.
Name the material which is used for making the filaments of an electric bulb.
The heat produced by passing an electric current through a fixed resistor is proportional to the square of:
(a) magnitude of resistance of the resistor
(b) temperature of the resistor
(c) magnitude of current
(d) time for which current is passed
Give Scientific reason.
In practice, the unit kWh is used for the measurement of electrical energy, rather than joule.
Solve the following example.
Two tungsten bulbs of wattage 100 W and 60 W power work on 220 V potential difference. If they are connected in parallel, how much current will flow in the main conductor?
The ‘live’ and the ‘neutral’ wires have potential difference of _______.
The electricity bill specifies the usage in _______.
These days when current in the circuit suddenly increases _______ switches are used.
Which of the following substance contracts on heating?
When does overloading occur?
Name some devices that run using heat effect of electric current
Heating effect of current is called ______
Mark the correct choice
- Assertion: Electric appliances with a metallic body have three wire connections.
- Reason: Three-pin connections reduce the heating of the connecting wires.
An electric kettle consumes 1 kW of electric power when operated at 220 V. A fuse wire of what rating must be used for it?
When a switch is in the OFF position,
(i) circuit starting from the positive terminal of the cell stops at the switch.
(ii) circuit is open.
(iii) no current flows through it.
(iv) current flows after some time. Choose the combination of the correct answers from the following.
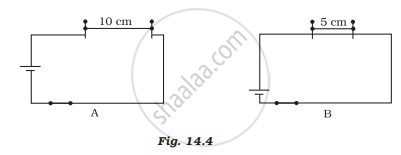
Paheli took a wire of length of 10 cm. Boojho took a wire of 5 cm of the same material and thickness. Both of them connected the wires as shown in the circuit given in Figure 14.4. The current flowing in both circuits is the same.
(i) Will the heat produced in both cases be equal? Explain
(ii) Will the heat produced be the same if the wires taken by them are of equal lengths but of different thicknesses? Explain.
______ wire is used in the filament of the bulbs.
Fuse is a strip of alloy wire which is made up of lead and tin with a very low ______.
Name a few appliances which work on the basis of the heating effect of current.
An electric fuse is a wire made up of a material having ______ melting point.
The electric fuse works on the Joule heating principle.
1 kWh is equal to ______.
What is the heating effect of electric current?
When a current I flows through a wire of resistance R for time t then the electrical energy produced is given by ______.
An electric iron is rated 220 V, 2 kW. If the iron is used for 3h daily find the cost of running it for one week if it costs ₹ 4.25 per kWh.
