Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Obtain an expression for the potential energy of a dipole in an external field.
उत्तर
- Consider a dipole with charges –q and +q separated by a finite distance 2l, placed in a uniform electric field `vec"E"`.
- It experiences a torque `vectau` which tends to rotate it as shown in figure below, `vec tau = vec"p" xx vec"E"` = pE sinθ
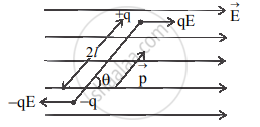
Couple acting on a dipole - To neutralize this torque, let us assume an external torque `vectau_"ext"` be applied, which rotates it in the plane of the paper from angle θ0 to angle θ, without angular acceleration and at an infinitesimal angular speed.
- Work done by the external torque
W = `int_{θ_0}^θ tau_"ext"(θ)"d"θ = int_{θ_0}^θ"pE" sinθ "d"θ`
= pE`[-cosθ]_{θ_0}^θ`
= pE`[-cosθ - (-cosθ_0)]`
= pE`[-cosθ + cosθ_0]`
= pE`[cosθ_0 - cosθ]`
This work done is stored as the potential energy of the system in the position when the dipole makes an angle θ with the electric field. - Thus, potential energy of electric dipole in external electric field is, U(θ) – U(θ0) = pE(cosθ0– cosθ)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A charge 6 µC is placed at the origin and another charge - 5 µC is placed on the y-axis at A = (0, 6.0 m).

(a) Calculate the net electric potential at P = (8.0 m, 0).
(b) Calculate the work done in bringing a proton from infinity to point P. What is the significance of the negative sign?
One hundred and twenty five small liquid drops, each carrying a charge of 0.5 µC and of diameter 0.1 m form a bigger drop. Calculate the potential at the surface of the bigger drop.
If an electron is brought towards another electron, the electric potential energy of the system ______.
Which physical quantity has its unit as J/C? Is it a scalar or vector?
Find the electric potential at the surface of an atomic nucleus (Z = 50) of radius 9 × 10-13 cm.
Three-point charges +q, +2q and Q are placed at the three vertices of an equilateral triangle. Find the value of charge Q (in terms of q), so that the electric potential energy of the system is zero.
Derive an expression for the electric potential due to an electric dipole.
An AC circuit contains resistance of 12Q and inductive reactance 5Q. The phase angle between current and potential difference will be ______.
In a certain region of space with volume 0.2 m3 , the electric potential is found to be 5V throughout. The magnitude of electric field in this region is: ____________.
The electric potential V at any point O (x, y, z all in metres) in space is given by V = 4x2 volt. The electric field at the point (1 m, 0, 2m) in volt/metre is ____________.
Two parallel plates separated by a distance 'd' are kept at potential difference 'V' volt. A charge 'q' of mass 'm' enters in parallel plates with some velocity. The acceleration of the charged particle will be ______
A capacitor C1 = 4µF is connected is series with another capacitor C2 = 1µF. The combination is connected across d.c. source of 200 V. The ratio of potential across C2 to that across C1 is ______.
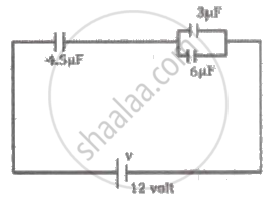
In the circuit shown, the potential difference across the 4.5 µF capacitor is ______.
Potential energy as a function of r is given by U = `"A"/"r"^10-"B"/"r"^5`, where r is the interatomic distance, A and B are positive constants. The equilibrium distance between the two atoms will be ______.
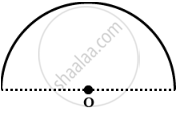
A semicircular wire of radius a having λ as charge per unit length is shown in the figure. Find the electric potential at the centre of the semicircular wire.
State the formula giving the relation between electric field intensity and potential gradient.
1 Weber/second is equal to ______.
Derive an expression for the electric potential energy of an electric dipole in a uniform electric field.
Derive the relation between electric intensity and electric potential.
