Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Plot a graph to show the variation of the angle of deviation as a function of the angle of incidence for light passing through a prism. Derive an expression for the refractive index of the prism in terms of angle of minimum deviation and angle of the prism.
उत्तर
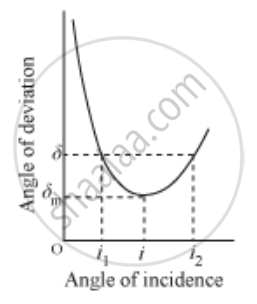
If the angle of incidence is increased gradually, then the angle of deviation first decreases, attains a minimum value (δm) and then again starts increasing.
When the angle of deviation is minimum, the prism is said to be placed in the minimum deviation position.
There is only one angle of incidence for which the angle of deviation is minimum.
When δ = δm [prism in minimum deviation position],
e = i and r2 = r1 = r …..(i)
∵ r1+r2=A
From (i), we get
r + r = A
`r=A/2`
Also, we have
A + δ = i + e
Substituting δ = δm and e = i,
A + δm = i + i
`i=(A+delta_m)/2`
∵`mu=sin i/sin r`
`:.mu=(sin(A+delta_m/2)/Sin (A/2))`
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the cause of dispersion of light
Can the dispersive power \[\omega = \frac{\mu_u - \mu_r}{\mu - 1}\] be negative? What is the sign of ω if a hollow prism is immersed into water?
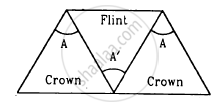
Three thin prisms are combined as shown in figure. The refractive indices of the crown glass for red, yellow and violet rays are μr, μy and μv respectively and those for the flint glass are μ'r, μ'y and μ'v respectively. Find the ratio A'/A for which (a) there is no net angular dispersion, and (b) there is no net deviation in the yellow ray.
A thin prism of crown glass (μr = 1.515, μv = 1.525) and a thin prism of flint glass (μr = 1.612, μv = 1.632) are placed in contact with each other. Their refracting angles are 5.0° each and are similarly directed. Calculate the angular dispersion produced by the combination.
A thin prism of angle 6.0°, ω = 0.07 and μy = 1.50 is combined with another thin prism having ω = 0.08 and μy = 1.60. The combination produces no deviation in the mean ray. (a) Find the angle of the second prism. (b) Find the net angular dispersion produced by the combination when a beam of white light passes through it. (c) If the prisms are similarly directed, what will be the deviation in the mean ray? (d) Find the angular dispersion in the situation described in (c).
A narrow beam of monochromatic light, PQ, is incident normally on one face of an equiangular glass prism of refractive index 1.45. When the prism is immersed in a certain liquid, the ray makes a grazing emergence along the other face (See figure). Find the refractive index of this liquid. 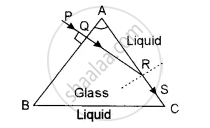
What is meant by the dispersive power of transparent material?
The refractive indices of material for red, violet and yellow colour light are 1.52, 1.62 and 1.59 respectively.
Calculate the dispersive power of the material. If the mean deviation is 40°. What will be the angular dispersion produced by a prism of this material?
For any prism, obtain a relation between the angle of the prism (A), the angle of minimum deviation (δm) and the refractive index of its material (μ or n).
When a ray of white light is incident obliquely on the first surface of a prism, then ______.
