Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the cause of dispersion of light
उत्तर
Cause of dispersion: Different colours of white light have different wavelengths. The wavelength of violet light is smaller than that of red light. The refractive index of a material in terms of the wavelength of the light is given by Cauchy’s expression.
`mu=a+b/lambda^2+c/lambda^4`
Here, a, b and c are constants for the material.
Thus, a material offers different refractive indices to lights of different wavelengths. This is the cause of dispersion of light
संबंधित प्रश्न
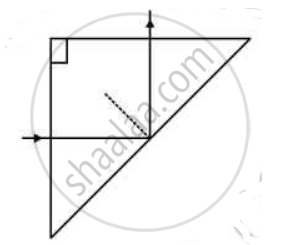
A ray of light incident normally on one face of a right isosceles prism is totally reflected, as shown in fig. What must be the minimum value of refractive index of glass? Give relevant calculations.
Describe an activity to show that the colours of white light splitted by a glass prism can be recombined to get white light by another identical glass prism. Also, draw a ray diagram to show the recombination of the spectrum of white light.
The equation \[\omega = \frac{\mu_u - \mu_r}{\mu - 1}\] was derived for a prism having small refracting angle. Is it also valid for a prism of large refracting angle? Is it also valid for a glass slab or a glass sphere?
The angular dispersion produced by a prism ___________ .
If a glass prism is dipped in water, its dispersive power ___________ .
Two prisms of identical geometrical shape are combined with their refracting angles oppositely directed. The materials of the prisms have refractive indices 1.52 and 1.62 for violet light. A violet ray is deviated by 1.0° when passes symmetrically through this combination. What is the angle of the prisms?
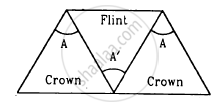
Three thin prisms are combined as shown in figure. The refractive indices of the crown glass for red, yellow and violet rays are μr, μy and μv respectively and those for the flint glass are μ'r, μ'y and μ'v respectively. Find the ratio A'/A for which (a) there is no net angular dispersion, and (b) there is no net deviation in the yellow ray.
The refractive index of a material M1 changes by 0.014 and that of another material M2 changes by 0.024 as the colour of the light is changed from red to violet. Two thin prisms, one made of M1(A = 5.3°) and the other made of M2(A = 3.7°) are combined with their refracting angles oppositely directed. (a) Find the angular dispersion produced by the combination. (b) The prisms are now combined with their refracting angles similarly directed. Find the angular dispersion produced by the combination.
The deviation produced for violet, yellow and red lights for crown glass are 3.75°, 3.25° and 2.86° respectively. Calculate the dispersive power of the crown glass.
A ray of light is incident on a prism whose refractive index is 1.52 at an angle of 40°. If the angle of emergence is 60°, calculate the angle of the prism.
