Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the cause of dispersion of light
उत्तर
Cause of dispersion: Different colours of white light have different wavelengths. The wavelength of violet light is smaller than that of red light. The refractive index of a material in terms of the wavelength of the light is given by Cauchy’s expression.
`mu=a+b/lambda^2+c/lambda^4`
Here, a, b and c are constants for the material.
Thus, a material offers different refractive indices to lights of different wavelengths. This is the cause of dispersion of light
संबंधित प्रश्न
A ray of light passes through an equilateral glass prism such that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence and each of these angles is equal to 3/4 of angle of prism. Find the angle of deviation.
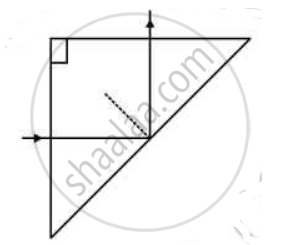
A ray of light incident normally on one face of a right isosceles prism is totally reflected, as shown in fig. What must be the minimum value of refractive index of glass? Give relevant calculations.
Describe an activity to show that the colours of white light splitted by a glass prism can be recombined to get white light by another identical glass prism. Also, draw a ray diagram to show the recombination of the spectrum of white light.
Give the formula that can be used to determine refractive index of materials of a prism in minimum deviation condition ?
The equation \[\omega = \frac{\mu_u - \mu_r}{\mu - 1}\] was derived for a prism having small refracting angle. Is it also valid for a prism of large refracting angle? Is it also valid for a glass slab or a glass sphere?
Can the dispersive power \[\omega = \frac{\mu_u - \mu_r}{\mu - 1}\] be negative? What is the sign of ω if a hollow prism is immersed into water?
The minimum deviations suffered by, yellow and violet beams passing through an equilateral transparent prism are 38.4°, 38.7° and 39.2° respectively. Calculate the dispersive power of the medium.
A thin prism of crown glass (μr = 1.515, μv = 1.525) and a thin prism of flint glass (μr = 1.612, μv = 1.632) are placed in contact with each other. Their refracting angles are 5.0° each and are similarly directed. Calculate the angular dispersion produced by the combination.
A narrow beam of monochromatic light, PQ, is incident normally on one face of an equiangular glass prism of refractive index 1.45. When the prism is immersed in a certain liquid, the ray makes a grazing emergence along the other face (See figure). Find the refractive index of this liquid. 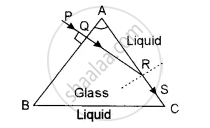
How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary if the incident violet light is replaced by red light?
