Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
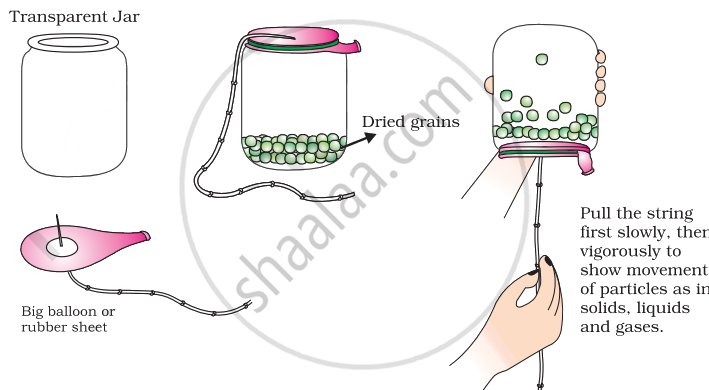
Prepare a model to demonstrate movement of particles in solids, liquids and gases.
For making this model you will need
- A transparent jar
- A big rubber balloon or piece of stretchable rubber sheet
- A string
- Few chickpeas or black gram or dry green peas.
How to make?
- Put the seeds in the jar.
- Sew the string to the centre of the rubber sheet and put some tape to keep it tied securely.
- Stretch and tie the rubber sheet on the mouth of the jar.
- Your model is ready. Now run your fingers up and down the string by first tugging at it slowly and then rapidly.
उत्तर
Materials Required:
- A transparent jar
- A big rubber balloon or piece of stretchable rubber sheet
- A string
- Few chickpeas, black gram, or dry green peas
Steps to Make the Model:
-
Prepare the Jar:
- Take a transparent jar and put the dried seeds (chickpeas, black gram, or dry green peas) into the jar. These seeds will represent the particles.
-
Attach the Rubber Sheet:
- Sew a string to the centre of the rubber balloon or rubber sheet.
- Secure the string tightly using some tape to ensure it stays attached.
- Stretch the rubber sheet over the mouth of the jar and tie it securely. This setup allows the rubber sheet to simulate the movement when the string is pulled.
-
Demonstrating Particle Movement:
- Your model is now ready.
- Gently pull the string attached to the rubber sheet and observe the movement of the seeds inside the jar.
- Start by tugging the string slowly to demonstrate the movement of particles in solids, where they move slightly.
- Then, pull the string more vigorously to demonstrate the movement of particles in liquids and gases, where they move more freely and rapidly.
This model effectively shows how particles in solids, liquids, and gases behave differently depending on the energy (represented by the speed of string pulling) applied to them.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Convert the following temperature to the celsius scale.
293 K
What do you mean by the change of state? Write the flow chart showing the complete cycle of change of state.
The boiling point of water is 100° C. Express this in SI units (Kelvin scale).
What is meant by saying that the latent heat of vaporisation of water is 22.5 × 105 J/kg ?
State whether the following statement is true or false :
Solid carbon dioxide is stored under low pressure.
Define the term 'latent heat of vaporisation' of a liquid. What is the value of the latent heat of vaporisation of water ?
What is sublimation ? Name two substances (other than ammonium chloride) which undergo sublimation.
Draw a labelled diagram of the experimental set-up to demonstrate the sublimation of ammonium chloride.
Explain the term boiling point
Fill in the blanks with the correct word/s from the bracket.
Ice on absorption of heat converts to ‘X’ a process called ____ [vaporization / melting]. ‘X’ changes to water vapour on ____ [heating / cooling]. Water vapour changes back to ‘X’ on ____ [freezing / condensation]. The constant temperature at which ice changes into ‘X’ is called its ____ [fusion point / melting point / boiling point].
