Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Prove that the points (–3, 0), (1, –3) and (4, 1) are the vertices of an isosceles right angled triangle. Find the area of this triangle
बेरीज
उत्तर
Let A (–3, 0), B (1, –3) and C (4, 1) be the given points. Then,
`AB=sqrt({1-(-3)}^2+(-3-0)^2)=sqrt(16+9)= `
`BC=sqrt((4-1)^2+(1+3)^2)=\sqrt{9+16}=`
`CA=sqrt((4+3)^2+(1-0)^2)=sqrt(49+1)=5\sqrt{2}`
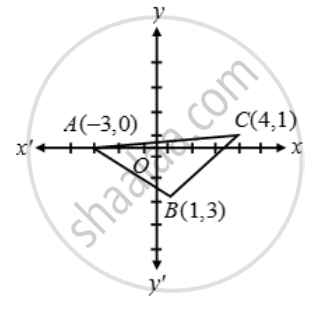
Clearly, AB = BC. Therefore, ∆ABC is isosceles.
Also,
`AB^2 + BC^2 = 25 + 25 = (5)^2 = CA^2`
⇒ ∆ABC is right-angled at B.
Thus, ∆ABC is a right-angled isosceles triangle.
Now,
`Area of ∆ABC = \frac { 1 }{ 2 } (Base × Height)`
`= \frac { 1 }{ 2 } (AB × BC)`
`⇒ Area of ∆ABC = \frac { 1 }{ 2 } × 5 × 5 sq. units`
`= \frac { 25 }{ 2 } sq. units`
shaalaa.com
या प्रश्नात किंवा उत्तरात काही त्रुटी आहे का?
