Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Read the newspaper report to find the following facts about Columbia’s ill-fated voyage.
Date of return journey: ____________
उत्तर
Date of return journey: 1st February, 2003
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Thinking about the Poem
What should we do to make friends with the wind?
Behrman has a dream. What is it? Does it come true?
What is the significance of the title?
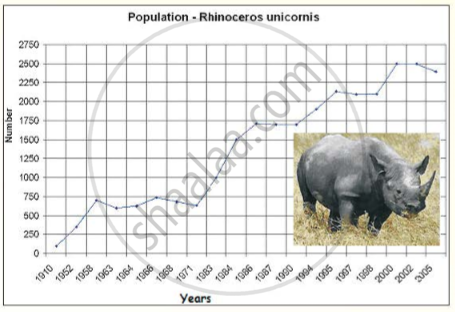
Read this article about the great Indian Rhinoceros. [You will find the information useful for your group discussion in 5.]
The Indian Rhinoceros or the Great One-Horned Rhinoceros or the Asian Onehorned Rhinoceros (Rhinoceros unicomis) is a large mammal primarily found in north-eastern India, Nepal and parts of Bhutan. It is confined to the tall grasslands and forests in the foothills of the Himalayas.
The Indian Rhinoceros once ranged throughout the entire stretch of the Indo Gangetic Plain but excessive hunting reduced their natural habitat drastically.
Today, about 3,000 Indian Rhinos live in the wild, 1,800 of which are found in Assam alone. In 2008, more than 400 Indian Rhinos were sighted in Nepal's Chitwan National Park.
In size it is equal to that of the White Rhino in Africa; together they are the largest of all rhino species. The Great One-Horned Rhinoceros has a single horn; this is present in both males and females, but not on newborn young. In most adults, the horn reachee a length of about 25 centimetres, but has been recorded up to 57 .2 centimetres in length. The nasal hom curves backwards from the nose. The horn is naturally black.
This prehistoric-looking rhinoceros bas thick, silver-brown skin which becomes pinkish near the large skin folds that cover its body. The male develops thick neckfolds. It has very little body hair aside from eyelashes, ear-fringes and tail-brush.
These rhinos live in tall grasslands and riverine forests, but due to the loss of habitat, they have been forced towards cultivated land. They are mostly solitary creatures, with the exception of mothers and calves and breeding pairs, although they sometimes, congregate at bathing areas.
The Indian Rhinoceros makes a wide variety of vocalizations. At least ten distinct vocalizations have been identified: snorting, honking, bleating, roaring, squeak panting, moo-grunting, shrieking, groaning, rumbling and humphing. In addition to noises, the rhino also uses olfactory communication.
In aggregation, Indian Rhinos are often friendly. They will often greet each other by waving or bobbing their heads, mounting flanks, nuzzling noses, or licking. Rhinos will playfully spar, run around, and play with twigs in their mouth. Adult males are the primary instigators of fights. Fights between dominant males are the most common cause of rhino mortality. Indian rhinos have few natural enemies, except for tigers. Tigers sometimes kill unguarded calves, but adult rhinos are less vulnerable due to their size. Humans are the only other animal threat, hunting the rhinoceros primarily for sport or for the use of its horn. Indian Rhinos have been somewhat tamed and trained in circuses, but they remain dangerous and unpredictable animals.
In the nineteenth and early twentieth century, the Indian Rhinoceros was hunted relentlessly. Reports from the middle of the nineteenth century claim that some military officers in Assam individually shot more than 200 rhinos. In the early 1900s, officials became concerned at the rhinos' plummeting numbers. By 1908 in Kaziranga, one of the Rhinos' main ranges, the population had fallen to around 12 individuals. In 1910, all rhino hunting in India became prohibited.
The rhino has been a major success in conservation. Only 100 remained in the early 1900s; a century later, their population has increased to about 2500 again, but even so, the species is still endangered. The Indian rhino is illegally poached for its horn. Some cultures in East Asia believe that the hair has healing and potency powers and therefore is used for traditional Chinese medicine and other Oriental medicines.
The Indian and Nepalese Governments have taken major steps towards Indian Rhinoceros conservation with the help of the World Wildlife Fund (WWF). The Kaziranga National Park and Manas National Park in Assam, Pobitora Reserve Forest in Assam {having the highest Indian rhino density in the world), Orang National Park of Assam, Laokhowa Reserve Forest of Assam (having a very small population) and Royal Chitwan National Park in Nepal are homes to this endangered animal.
Exceeding peace had made Ben Adhem bold,
And to the presence in the room he said,
"What writest thou?"..... The vision raised its head,
And with a look made of all sweet accord,
Answered, "The names of those who love the Lord."
Read the lines given above and answer the following question.
What did Abou Adhem ask the angel?
Then there it lay in her wet palm, perfect, even pierced ready for use, with the sunset shuffled about inside it like gold—?dust. All her heart went up in flames of joy. After a bit she twisted it into the top of her skirt against her tummy so she would know if it burst through the poor cloth and fell. Then she picked up her fork and sickle and the heavy grass and set off home. Ai! Ai! What a day! Her barefeet smudged out the wriggle— ?mark of snakes in the dust; there was the thin singing of malaria mosquitoes among the trees now; and this track was much used at night by a morose old makna elephant—the Tuskless One; but Sibia was not thinking of any of them. The stars came out: she did not notice. On the way back she met her mother, out of breath, come to look for her, and scolding. “I did not see till I was home, that you were not there. I thought something must have happened to you.” And Sibia, bursting with her story, cried “Something did). I found a blue bead for my necklace, look!”
Read the extract given below and answer the question that follow.
Is the Ending Appropriate?
The phrases on the left in the following box occur in the text. Match each of them with a phrase on the right.
| (i) an endless stretch of sand | •fertile place with water and plants in a desert |
| (ii) waterless and without shelter | •not visible because the grass is thick |
| (iii) an oasis | •nothing but sand as far as one can see |
| (iv) hidden by a cover of grass | •no water and no shade |
The tiger was still licking his arm, with increasing relish. The phrase in underlined suggests that Timothy
Find in the poem lines that match the following. Read both one after the other.
He is noisy on purpose
What were the replies the king received for his first question?
How do the desert plants fulfill their need for water?
How did the crocodile plan to please his wife? How did the monkey use his wits and save his life?
Define a dream in your own words.
Why did the Dog say goodbye to the Wolf?
Mark the right item:
“This, said the emperor, was to encourage all children to honour and obey their parents.”
‘This’ refers to ______
Answer the following question.
“Each term every child has one blind day, one lame day…” Complete the line. Which day was the hardest? Why was it the hardest?
What was the real aim of Miss Beam’s school?
Answer the question.
What does he imagine about
what they do at home?
Discuss the posture of the squirrel as discussed in line 3 of the poem.
With close reference to Act V, describe how Prospero has used the spirits of "hills, brooks, groves" to give shape to his magical acts. What does he finally decide to do with his magical powers?
