Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
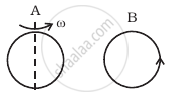
Same as problem 4 except the coil A is made to rotate about a vertical axis (figure). No current flows in B if A is at rest. The current in coil A, when the current in B (at t = 0) is counterclockwise and the coil A is as shown at this instant, t = 0, is ______.
पर्याय
constant current clockwise.
varying current clockwise.
varying current counterclockwise.
constant current counterclockwise.
उत्तर
Same as problem 4 except the coil A is made to rotate about a vertical axis (figure). No current flows in B if A is at rest. The current in coil A, when the current in B (at t = 0) is counterclockwise and the coil A is as shown at this instant, t = 0, is constant current clockwise.
Explanation:
In this problem, Lenz’s law is applicable so let us introduce Lenz’s law first.
Lenz’s law gives the direction of induced emf/induced current. According to this law, the direction of induced emf or current in a circuit is such as to oppose the cause that produces it. This law is based upon law of conservation of energy.
When the current in coil B (at t = 0) is counter-clockwise and coil A is considered above it. The counterclockwise flow of the current in coil B is equivalent to north pole of magnet and magnetic field lines are eliminated upward to coil A. When coil A starts rotating at t = 0, the current in A is constant along a clockwise direction by Lenz’s rule.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
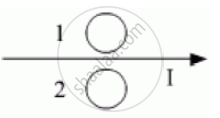
Predict the directions of induced currents in metal rings 1 and 2 lying in the same plane where current I in the wire is increasing steadily.
Explain, with the help of a suitable example, how we can show that Lenz's law is a consequence of the principle of conservation of energy.
Young's modulus for aluminium is 7 × 1010 Pa. The force needed to stretch an aluminium wire of diameter 2 mm and length 800 mm by 1 mm is ______.
A bar magnet is dropped through a copper ring acceleration of magnet is
Energy dissipate in LCR circuit in
For a coil having L = 2 mH, current flows at the rate of 10-3 AIS. The e.m.f induced is
There are two coils A and B as shown in figure. A current starts flowing in B as shown, when A is moved towards B and stops when A stops moving. The current in A is counterclockwise. B is kept stationary when A moves. We can infer that ______.

A wire in the form of a tightly wound solenoid is connected to a DC source, and carries a current. If the coil is stretched so that there are gaps between successive elements of the spiral coil, will the current increase or decrease? Explain.
Consider a metal ring kept on top of a fixed solenoid (say on a carboard) (Figure). The centre of the ring coincides with the axis of the solenoid. If the current is suddenly switched on, the metal ring jumps up. Explain
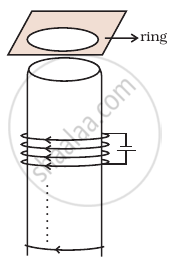
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.