Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
There are two coils A and B as shown in figure. A current starts flowing in B as shown, when A is moved towards B and stops when A stops moving. The current in A is counterclockwise. B is kept stationary when A moves. We can infer that ______.

पर्याय
there is a constant current in the clockwise direction in A.
there is a varying current in A.
there is no current in A.
there is a constant current in the counterclockwise direction in A.
उत्तर
There are two coils A and B as shown in figure. A current starts flowing in B as shown, when A is moved towards B and stops when A stops moving. The current in A is counterclockwise. B is kept stationary when A moves. We can infer that there is a constant current in the counterclockwise direction in A.
Explanation:
Due to variation in the flux linked with coil B an emf will be induced in coil B. Current in coil B becomes zero when coil A stops moving, it is possible only if the current in coil A is constant. If the current in coil A would be variable, there must be some changing flux and then there must be an induced emf. Hence an induced current will be in coil B even when coil A is not moving.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Lenz's law. Illustrate, by giving an example, how this law helps in predicting the direction of the current in a loop in the presence of a changing magnetic flux.
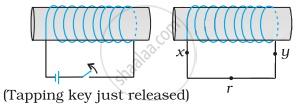
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.
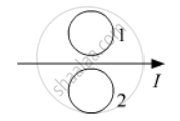
What is the direction of induced currents in metal rings 1 and 2 when current I in the wire is increasing steadily?
Predict the direction of induced current in a metal ring when the ring is moved towards a straight conductor with constant speed v. The conductor is carrying current I in the direction shown in the figure.
Predict the direction of induced current in metal rings 1 and 2 when current I in the wire is steadily decreasing?
A short magnet is moved along the axis of a conducting loop. Show that the loop repels the magnet if the magnet is approaching the loop and attracts the magnet if it is going away from the loop.
The battery discussed in the previous question is suddenly disconnected. Is a current induced in the other loop? If yes, when does it start and when does it end? Do the loops attract each other or repel?
Lenz's law gives ______
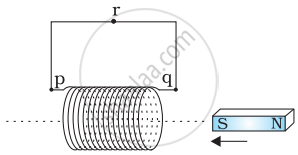
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.