Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
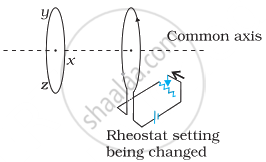
The battery discussed in the previous question is suddenly disconnected. Is a current induced in the other loop? If yes, when does it start and when does it end? Do the loops attract each other or repel?
उत्तर
When the battery is suddenly disconnected, a current is induced in loop B due to a sudden change in the flux through it. It is only induced for a moment when the current suddenly falls to zero. There is no induced current after it has fallen to zero. According to Lenz's law, the induced current is such that it increases the decreasing magnetic field. So, if the current in loop A is in clockwise direction, the induced current in loop B will also be in clockwise direction. Hence, the two loops will attract each other.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Lenz's law. Illustrate, by giving an example, how this law helps in predicting the direction of the current in a loop in the presence of a changing magnetic flux.
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.
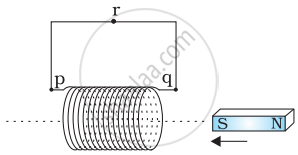
Use Lenz’s law to determine the direction of induced current in the situation described by the figure:
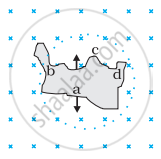
A wire of irregular shape turning into a circular shape.
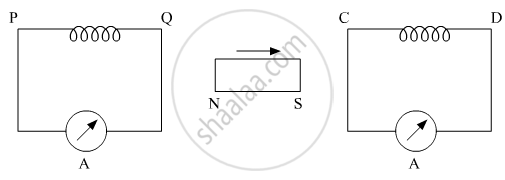
A bar magnet is moved in the direction indicated by the arrow between two coils PQ and CD. Predict the directions of induced current in each coil.
Consider the situation shown in figure. If the switch is closed and after some time it is opened again, the closed loop will show ____________ .
A bar magnet is moved along the axis of a copper ring placed far away from the magnet. Looking from the side of the magnet, an anticlockwise current is found to be induced in the ring. Which of the following may be true?
(a) The south pole faces the ring and the magnet moves towards it.
(b) The north pole faces the ring and the magnet moves towards it.
(c) The south pole faces the ring and the magnet moves away from it.
(d) The north pole faces the ring and the magnet moves away from it.
Lenz’s law is a consequence of the law of conservation of ______.
2 A 40 kg boy whose legs are 4 cm in area and 50 cm long falls through a height of 2 m without breaking his leg bones. If the bones can withstand stress of 0.9 x 108 N/m2. The Young's modulus for the material of the bone is ______.
Lenz's law gives ______
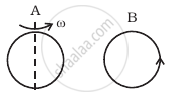
There are two coils A and B as shown in figure. A current starts flowing in B as shown, when A is moved towards B and stops when A stops moving. The current in A is counterclockwise. B is kept stationary when A moves. We can infer that ______.

Same as problem 4 except the coil A is made to rotate about a vertical axis (figure). No current flows in B if A is at rest. The current in coil A, when the current in B (at t = 0) is counterclockwise and the coil A is as shown at this instant, t = 0, is ______.
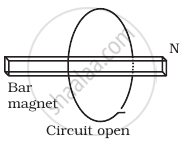
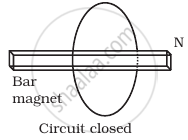
Consider a magnet surrounded by a wire with an on/off switch S (Figure). If the switch is thrown from the off position (open circuit) to the on position (closed circuit), will a current flow in the circuit? Explain.
A wire in the form of a tightly wound solenoid is connected to a DC source, and carries a current. If the coil is stretched so that there are gaps between successive elements of the spiral coil, will the current increase or decrease? Explain.
Consider a metal ring kept on top of a fixed solenoid (say on a carboard) (Figure). The centre of the ring coincides with the axis of the solenoid. If the current is suddenly switched on, the metal ring jumps up. Explain
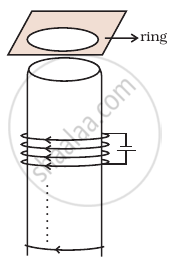
A long solenoid ‘S’ has ‘n’ turns per meter, with diameter ‘a’. At the centre of this coil we place a smaller coil of ‘N’ turns and diameter ‘b’ (where b < a). If the current in the solenoid increases linearly, with time, what is the induced emf appearing in the smaller coil. Plot graph showing nature of variation in emf, if current varies as a function of mt2 + C.
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.