Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Select the correct statement
पर्याय
Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food
Heterotrophs utilise solar energy for photosynthesis
Heterotrophs synthesise their own food
Heterotrophs are capable of converting carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates
उत्तर
Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food
Explanation -
Heterotrophs are food-dependent on either Phototrophs or other species.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The food synthesised by the plants is stored as ______.
Arrange the following processes involved in the nutrition in animals in the correct order (in which they take place):
Assimilation, Egestion, Ingestion, Absorption, Digestion
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
All non-green plants and animals are ....................
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Heterotrophs depend on .................... and other .................... for food.
What are herbivores, carnivores and omnivores? Give two examples of each.
The correct order of steps occurring in nutrition in animals is:
(a) Ingestion → Absorption → Digestion → Assimilation → Egestion
(b) Ingestion → Digestion → Assimilation → Absorption → Egestion
(c) Ingestion → Digestion → Absorption → Assimilation → Egestion
(d) Ingestion → Assimilation → Digestion → Absorption → Egestion
A unicellular animal P having no fixed shape ingests a food particle by forming temporary finger-like projections Q. The food particle is engulfed with a little surrounding water to form a temporary stomach R inside it. The chemicals S from surrounding cytoplasm enter into R and break down food into small and soluble molecules by chemical reactions. The digested food is absorbed directly into cytoplasm by the process T. The undigested food is thrown out of the body by the rupture of a cell organelle U in a process called V.
(a) Name the unicellular animal P.
(b) What are (i) Q, and (ii) R?
(c) Name (i) chemical S, and (ii) process T.
(d) Name (i) organelle U, and (ii) process V.
X is a wild animal which eats only the flesh of other animals whereas Y is a domestic animal which feeds mainly on green grass.
(a) What are animals like X known as?
(b) What are animals Y known as?
(c) Which animal, X or Y, has a longer small intestine? Why?
(d) Name one animal which is like X.
(e) Name one animal which is like Y.
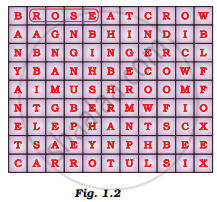
Spot as many organisms as possible in the puzzle given in Figure 1.2 by encircling them as shown. Write the names on a sheet of paper and categorise them into autotrophs and heterotrophs. Classify the heterotrophs into herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and saprophytes.
Patients whose gallbladder are removed are recommended to eat less oily food. Why?
