Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following problem.
A magnetic pole of a bar magnet with a pole strength of 100 A m is 20 cm away from the centre of a bar magnet. The bar magnet has a pole strength of 200 A m and has a length of 5 cm. If the magnetic pole is on the axis of the bar magnet, find the force on the magnetic pole.
उत्तर
Given that, (qm)1 = 200 Am and
(2l) = 5 cm = 5 × 10–2 m
∴ m = 200 × 5 × 10–2 = 10 Am2
For a bar magnet, magnetic dipole moment is,
m = qm (2l)
For a point on the axis of a bar magnet at distance, r = 20 cm = 0.2 m,
Ba = `μ_0/(4π)xx(2"m")/"r"^3`
= `10^-7xx(2xx10)/(0.2)^3`
= 0.25 × 10−3
= 2.5 × 10−4 Wb/m2
The force acting on the pole will be given by,
F = qm Ba = 100 × 2.5 × 10–4
= 2.5 × 10–2 N
The force acting on the magnetic pole due to the bar magnet is 2.5 × 10–2 N.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write any three properties of magnetic lines of force.
An iron needle is attracted to the ends of a bar magnet but not to the middle region of the magnet. Is the material making up the ends of a bare magnet different from that of the middle region?
Answer the following question.
Write the four important properties of the magnetic field lines due to a bar magnet.
An electron moves along +x direction. It enters into a region of uniform magnetic field. `vecB` directed along –z direction as shown in fig. Draw the shape of the trajectory followed by the electron after entering the field.
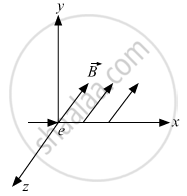
Answer the following question in brief.
What happens if a bar magnet is cut into two pieces transverse to its length/along its length?
Answer the following question in detail.
A circular magnet is made with its north pole at the centre, separated from the surrounding circular south pole by an air gap. Draw the magnetic field lines in the gap.
Answer the following question in detail.
Two bar magnets are placed on a horizontal surface. Draw magnetic lines around them. Mark the position of any neutral points (points where there is no resultant magnetic field) on your diagram.
A closely wound solenoid of 800 turns and area of cross-section 2.5 × 10–4 m2 carries a current of 3.0 A. Explain the sense in which the solenoid acts like a bar magnet. What is its associated magnetic moment?
A closely wound solenoid of 2000 turns and area of cross-section 1.6 × 10–4 m2, carrying a current of 4.0 A, is suspended through its centre allowing it to turn in a horizontal plane.
- What is the magnetic moment associated with the solenoid?
- What is the force and torque on the solenoid if a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 7.5 × 10–2 T is set up at an angle of 30° with the axis of the solenoid?
Which of the following statements about bar magnet is correct?
When iron filings are sprinkled on a sheet of glass placed over a short bar magnet then, the iron filings form a pattern suggesting that the magnet has ______.
According to the dipole analogy 1/ε0 corresponds to ______.
The resistance of ideal voltmeter is
At a certain 100 p of reduces 0.0/57 m carrier a current of 2 amp. The magnetic field at the centre of the coop is [`mu_0 = 4pi xx 10^-7` wb/amp – m]
When current is double deflection is also doubled in
A magnetic needle suspended freely orients itself:-
A bar magnet of magnetic moment 3.0 Am is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 2 × 10-5T. If each pole of the magnet experience a force of 6 × 10-4 N, the length of the magnet is ______.
Magnetic dipole moment is a ______
A bar magnet of magnetic moment m and moment of inertia I (about centre, perpendicular to length) is cut into two equal pieces, perpendicular to length. Let T be the period of oscillations of the original magnet about an axis through the midpoint, perpendicular to length, in a magnetic field B. What would be the similar period T′ for each piece?
There are two current carrying planar coils made each from identical wires of length L. C1 is circular (radius R) and C2 is square (side a). They are so constructed that they have same frequency of oscillation when they are placed in the same uniform B and carry the same current. Find a in terms of R.
A long straight wire of circular cross section of radius 'a' carries a steady current I. The current is uniformly distributed across its cross section. The ratio of magnitudes of the magnetic field at a point `a/2` above the surface of wire to that of a point `a/2` below its surface is ______.
A bar magnet is demagnetized by inserting it inside a solenoid of length 0.2 m, 100 turns, and carrying a current of 5.2 A. The coercivity of the bar magnet is ______.
