Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State and define Ohm’s law.
उत्तर
Ohm’s law states that at a constant temperature, the current flowing in a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends, i.e., if the potential difference is halved, the current is also halved and if p.d. is doubled, the current is also doubled, i.e.,
V (potential difference) ∝ i (current)
Or V = iR, where R is constant, called the resistance of the conductor.
So V = iR represents Ohm’s law.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
What is an Ohmic resistor?
The resistors R1, R2, R3 and R4 in the figure given below are all equal in value.
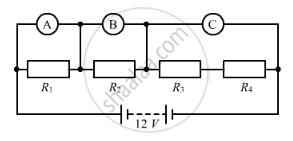
What would you expect the voltmeter A, B and C to read assuming that the connecting wires in the circuit have negligible resistance?
A car bulb connected to a 12 volt battery draws 2 A current when glowing. What is the resistance of the filament of the bulb? Will the resistance be more same or less when the bulb is not glowing?
Calculate the current flowing through a wire of resistance 5 Ω connected to a battery of potential difference 3 V.
A wire of resistance 3 ohm and length 10 cm is stretched to length 30 cm. Assuming that it has a uniform cross section, what will be its new resistance?
A wire has a length of 2.0 m and a resistance of 5.0 Ω. Find the electric field existing inside the wire if it carries a current of 10 A.
Define the following:
(i) Coulomb
(ii) Ohm
What is the resistance of a conductor through which a current of 0.5 A flows when a potential difference of 2V is applied across its ends?
