Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State and define Ohm’s law.
Solution
Ohm’s law states that at a constant temperature, the current flowing in a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends, i.e., if the potential difference is halved, the current is also halved and if p.d. is doubled, the current is also doubled, i.e.,
V (potential difference) ∝ i (current)
Or V = iR, where R is constant, called the resistance of the conductor.
So V = iR represents Ohm’s law.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A low voltage supply from which one needs high currents must have very low internal resistance. Why?
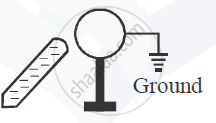
A metal sphere is kept on an insulting stands. A negatively charged rod is brought near it, then the sphere is earthed as shown. On removing the earthing, and taking the negatively charged rod away, what will be the nature of charge on the sphere? Give reason for your answer.
Define Current density.
Obtain the macroscopic form of Ohm’s law from its microscopic form and discuss its limitation.
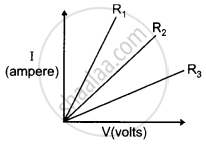
A student carries out an experiment and plots the V-I graph of three samples of nichrome wire with resistances R1, R2 and R3 respectively. Which of the following is hue?
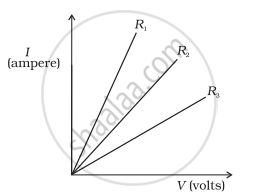
A student carries out an experiment and plots the V-I graph of three samples of nichrome wire with resistances R1, R2 and R3 respectively. Which of the following is true?

Vinita and Ahmed demonstrated a circuit that operates the two headlights and the two sidelights of a car, in their school exhibition. Based on their demonstrated circuit, answer the following questions.
- State what happens when switch A is connected to:
a) Position 2
b) Position 3 - Find the potential difference across each lamp when lit.
- Calculate the current.
a) in each 12 Ω lamp when lit.
b) In each 4 Ω lamp when lit.
OR - Show, with calculations, which type of lamp, 4.0 Ω or 12 Ω, has the higher power.
The voltage - current readings of a certain material are shown in the table given below:
| Voltage (V) | 10 V | 20 V | 30 V |
| Current (I) | 2 A | 3 A | 4 A |
Study the table.
- State whether the conductor used is ohmic or non-ohmic.
- Justify your answer.
- State Ohm's law.
