Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State and explain the laws of resistance.
उत्तर
The following are the main laws of resistance:
(i) Resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to its length, provided temperature and other physical conditions remain unchanged.
It means that R ∝ l i.e., if the length increases, the resistance also increases and if length decreases, its resistance also decreases.
(ii) Resistance of a conductor is inversely proportional to its area of cross section, other conditions remaining the same.
If A is the area of cross section, then:
R α `1/"A"`
or R α `1/(pi"r"^2)`
where r is the radius of the wire
Keeping the length same, if the radius of the wire is doubled then:
R α `1/(2"r")^2` α `1/"4r"^2`
or R α `1/4 . 1/(pi"r"^2)`, or R becomes one fourth.
Similarly if r is made half, then:
R α `1/("r"/2)^2`
α `4/"r"^2 α 4 (1/"r"^2)`, orR becomes 4 times
This shows that R is α `1/"A"`
(iii) R depends on the nature of the material of the conductor. It means, if we take equal lengths of wires of copper, aluminium and iron and all of the same cross-sectional area, their resistance are different from each other since they are of different materials.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
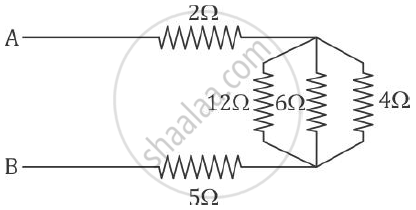
Find the equivalent resistance between points A and B.
State the order of resistivity of (i) a metal, (ii) a semiconductor and (iii) an insulator.
Why are thick copper wires used as connecting wires?
How does the resistivity of an alloy such as constantace depends on temperature.
State expression for Resistance connected in parallel.
State expression for Cells connected in parallel.
What is a resistance? Define it with respect to Ohm’s law,
You are provided with three resistors of resistance 1.0 Ω, 2.0 Ω and 3.0 Ω How would you connect them to obtain the total effective resistance 1.5 Ω? Draw diagram of the arrangement and check it by calculations.
2Ω resistor A, 1Ω resistor B and 4Ω resistor C are connected in parallel. The combination is connected across a 2V battery of negligible resistance. Draw the diagram of the arrangement and calculate:
(i) The current in each resistor A and C,
(ii) The current through battery.
A metal wire of resistance 6 Ω is stretched so that its length is increased to twice its original length. Calculate its new resistance.
