Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State Gauss's theorem in electrostatics. Using this theorem, derive an expression for the electric field due to an infinitely long straight wire of linear charge density λ.
उत्तर
Gauss’s theorem: The flux of an electric field through any closed surface is `1/(epsilon_0)` times the total charge enclosed by the closed surface.
`phi = q/(epsilon_0)` ...(1)
By definition, the total electric flux through the closed surface is given by
`phi = "∮"vecE*vec(ds)` ...(2)
∴ From (1) and (2), Gauss’s theorem may be expressed as follows
`phi = "∮"vecE*vec(ds) = q/epsilon_0`
∴ The surface integral of electric field over a closed surface is equal to `1/epsilon_0` times the total charge enclosed by the surface.
Application of Gauss’s theorem:
To find electric field due to a line charge, let us consider an infinitely long line charge placed along XX’ axis with linear charge density λ. Our aim is to find electric field intensity at a point P distant r from the line charge. We draw a cylindrical surface of radius r and length l coaxial with the line charge. The net flux through the cylindrical gaussian surface, i.e.
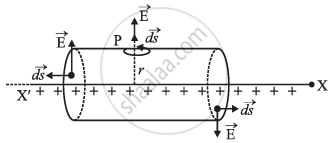
`phi = "∮"vecE*vec(ds)`
= `int_(LCF)vecE*vec(ds) + int_(CS)vecE*vec(ds) + int_(RCF)vecE*vec(ds)`
= `int_(LCF)Eds cos90"°" + int_(CS)Eds cos0"°" + int_(RCF)Eds cos90"°"`
`phi = int_(CS)Eds cos0"°" = E*2pirl` ...(1)
The charge enclosed by the gaussian surface is q = λl ...(2)
Using Gauss’s theorem from equations (1) and (2)
`E*(2pirl)= (lambdal)/epsilon_0 ⇒ E = lambda/(2piepsilon_0r)`
