Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2024-2025
Date: मार्च 2025
Advertisements
General Instruction:
- There are 33 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D and Section E.
- All the sections are compulsory.
- Section A contains sixteen questions, twelve MCQ and four Assertion Reasoning based of 1 mark each, Section B contains five questions of two marks each, Section C contains seven questions of three marks each, Section D contains two case study-based questions of four marks each and Section E contains three long answer questions of five marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question in Section B, one question in Section C, one question in each CBQ in Section D and all three questions in Section E. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
- Use of calculators is not allowed.
- You may use the following values of physical constants where ever necessary
- c = 3 × 108 m/s
- me = 9.1 × 10-31 kg
- mp = 1.7 × 10-27 kg
- e = 1.6 × 10-19 C
- μ0 = 4π × 10-7T m A-1
- h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js
- ε0 = 8.854 × 10-12C2N-1m-2
- Avogadro's number = 6.023 × 1023 per gram mole
A uniform electric field pointing in positive X-direction exists in a region. Let A be the origin, B be the point on the X-axis at X = +1 cm and C be the point on the Y-axis at y = +1 cm. Then the potential at points A, B and C satisfy.
VA < VB
VA > VB
VA < VC
VA > VC
Chapter:
A conducting wire connects two charged conducting spheres of radii r1 and r2 such that they attain equilibrium with respect to each other. The distance of separation between the two spheres is very large as compared to either of their radii.
The ratio of the magnitudes of the electric fields at the surfaces of the spheres of radii r1 and r2 is:
`(r_1)/(r_2)`
`(r_2)/(r_1)`
`r_2^2/r_1^2`
`r_1^2/r_2^2`
Chapter:
A long straight wire of circular cross section of radius 'a' carries a steady current I. The current is uniformly distributed across its cross section. The ratio of magnitudes of the magnetic field at a point `a/2` above the surface of wire to that of a point `a/2` below its surface is ______.
4 : 1
1 : 1
4 : 3
3 : 4
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
The diffraction effect can be observed in ______.
sound waves only
light waves only
ultrasonic waves only
sound waves as well as light waves
Chapter:
A capacitor consists of two parallel plates with an area of cross-section of 0.001 m2, separated by a distance of 0.0001 m. If the voltage across the plates varies at the rate of 108 V/s, then the value of displacement current through the capacitor is ______.
8.85 × 10−3 A
8.85 × 10−4 A
7.85 × 10−3 A
7.85 × 10−3 A
Chapter:
In a series LCR circuit, the voltage across the resistance, capacitance and inductance is 10 V each. If the capacitance is short circuited, the voltage across the inductance will be ______.
10 V
`10sqrt2 V`
`10//sqrt2 V`
20 V
Chapter:
Correct match of column I with column II is:
| C-l (waves) | C-ll (Production) | ||
| (1) | Infra-red | P. | Rapid vibration of electrons in aerials |
| (2) | Radio | Q. | Electrons in atoms emit light when they move from higher to lower energy levels. |
| (3) | Light | R. | Klystron valve |
| (4) | Microwave | S. | Vibration of atoms and molecules |
1 - P, 2 - R, 3 - S, 4 - Q
1 - S, 2 - P, 3 - Q, 4 - R
1 - Q, 2 - P, 3 - S, 4 - R
1 - S, 2 - R, 3 - P, 4 - Q
Chapter:
The distance of the closest approach of an alpha particle is d when it moves with a speed V towards a nucleus.
Another alpha particle is projected with higher energy, such that the new distance of the closest approach is `d/2`. What is the speed of projection of the alpha particle in this case?
`V/2`
`sqrt2V`
2 V
4 V
Chapter:
A point object is placed at the centre of a glass sphere of radius 6 cm and refractive index 1.5. The distance of the virtual image from the surface of the sphere is ______.
2 cm
4 cm
6 cm
12 cm
Chapter:
Colours observed on a CD (Compact Disk) is due to ______.
Reflection
Diffraction
Dispersion
Absorption
Chapter:
The number of electrons made available for conduction by dopant atoms depends strongly upon ______.
doping level
increase in ambient temperature
energy gap
doping level and increase in ambient temperature
Chapter:
If copper wire is stretched to make its radius decrease by 0.1%, then the percentage change in its resistance is approximately ______.
−0.4%
+0.8%
+0.4%
+0.2%
Chapter:
Assertion (A): On Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer by increasing the number of turns may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity.
Reason (R): The resistance of the coil of the galvanometer increases on increasing the number of turns.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false and R is also false.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Assertion (A): In a hydrogen atom there is only one electron but its emission spectrum shows many lines.
Reason (R): In a given sample of hydrogen there are many atoms each containing one electron; hence many electrons in different atoms may be in different orbits so many transitions from higher to lower orbits are possible.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): Nuclei having mass number about 60 are least stable.
Reason (R): When two or more light nuclei are combined into a heavier nucleus then the binding energy per nucleon will decrease.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): de Broglie's wavelength of a freely falling body keeps decreasing with time.
Reason (R): The momentum of the freely falling body increases with time.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Chapter:
A platinum surface having work function 5.63 eV is illuminated by a monochromatic source of 1.6 × 1015 Hz. What will be the minimum wavelength associated with the ejected electron?
Chapter:
A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths, 4000 Å and 6000 Å, is used to obtain interference fringes in a Young’s double-slit experiment. What is the least distance from the central maximum where the dark fringe is obtained?
Chapter:
In Young’s double-slit experiment using monochromatic light of wavelength λ, the intensities of two sources are I. What is the intensity of light at a point where the path difference between wavefronts is `lambda/4`?
Chapter:
P and Q are two identical charged particles each of mass 4 × 10–26 kg and charge 4.8 × 10–19 C, each moving with the same speed of 2.4 × 105 m/s as shown in the figure. The two particles are equidistant (0.5 m) from the vertical Y-axis. At some instant, a magnetic field B is switched on so that the two particles undergo head-on collision.
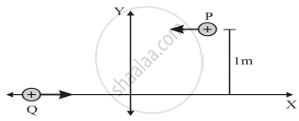
Find –
- the direction of the magnetic field and
- the magnitude of the magnetic field applied in the region.
Chapter:
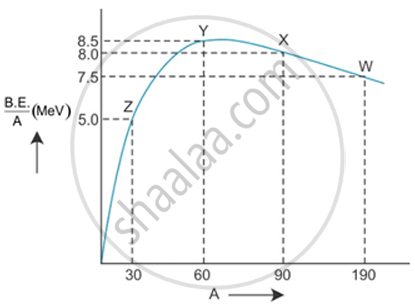
Binding energy per nucleon vs mass number curve for nuclei is shown in the figure. W, X, Y and Z are four nuclei indicated on the curve. Identify which of the following nuclei is most likely to undergo
- Nuclear Fission
- Nuclear Fusion.
Justify your answer.
Chapter:
A cylindrical conductor of length l and cross-section area A is connected to a DC source. Under the influence of an electric field set up due to the source, the free electrons begin to drift in the opposite direction of the electric field.
- Draw the curve showing the dependency of drift velocity on relaxation time.
- If the DC source is replaced by a source whose current changes its magnitude with time such that I = I0 sin 2πvt, where v is the frequency of variation of current, then determine the average drift velocity of the free electrons over one complete cycle.
Chapter:
Advertisements
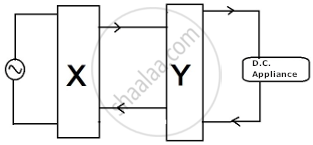
Identify the circuit elements X and Y as shown in the given block diagram and draw the output waveforms of X and Y.
Chapter:
If the centre tapping is shifted towards Diode D1 as shown in the diagram, draw the output waveform of the given circuit.

Chapter:
Find the expression for the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor of plate area A and plate separation d when
- a dielectric slab of thickness t and
- a metallic slab of thickness t,
where (t < d) are introduced one by one between the plates of the capacitor. In which case would the capacitance be more and why?
Chapter:
- Draw a ray diagram for the formation of image by a Cassegrain telescope.
- Why these types of telescopes are preferred over refracting type telescopes.
Chapter:
Draw the energy band diagram for P-type semiconductor at T = 0K.
Chapter:
Draw the energy band diagram for P-type semiconductor at room temperature.
Chapter:
In the given diagram, considering an ideal diode, in which condition will the bulb glow?
- When the switch is open.
- When the switch is closed.
Justify your answer.
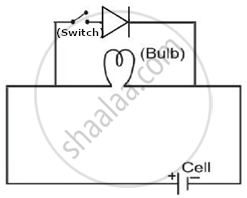
Chapter:
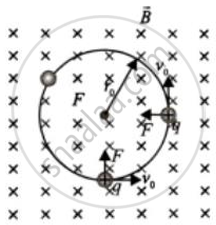
A boy is holding a smooth, hollow and non-conducting pipe vertically with a charged spherical ball of mass 10 g carrying a charge of +10 mC inside it, which is free to move along the axis of the pipe. The boy is moving the pipe from East to West direction in the presence of a magnetic field of 2T. With what minimum velocity should the boy move the pipe such that the ball does not move along the axis? Also determine the direction of the magnetic field.
Chapter:
A light ray entering a right-angled prism undergoes refraction at the face AC, as shown in Fig. 1.
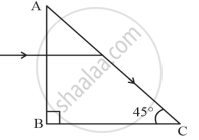
Fig. 1
- What is the refractive index of the material of the prism in Fig. 1?
-
- If the side AC of the above prism is now surrounded by a liquid of refractive index `2/sqrt3`, as shown in Fig. 2, determine if the light ray continues to graze along the interface AC or undergoes total internal reflection, or undergoes refraction into the liquid.
Fig. 2 - Draw the ray diagram to represent the path followed by the incident ray with the corresponding angle values.
`["Given," sin^-1(sqrt2/sqrt3 ) = 54.6°]`
- If the side AC of the above prism is now surrounded by a liquid of refractive index `2/sqrt3`, as shown in Fig. 2, determine if the light ray continues to graze along the interface AC or undergoes total internal reflection, or undergoes refraction into the liquid.
Chapter:
State Gauss's theorem in electrostatics. Using this theorem, derive an expression for the electric field due to an infinitely long straight wire of linear charge density λ.
Chapter:
Define Electric Flux. Write its SI unit.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Use Gauss's law to obtain the expression for the electric field due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet of charge.
Chapter:
|
An electron with speed v0 << c moves in a circle of radius r0 in a uniform magnetic field. This electron is able to traverse a circular path as the magnetic force acting on the electron is perpendicular to both v0 and B, as shown in the figure. This force continuously deflects the particle sideways without changing its speed and the particle will move along a circle perpendicular to the field. The time required for one revolution of the electron is T0.
|
If the speed of the electron is now doubled to 2v0. The radius of the circle will change to ______.
4r0
2r0
r0
`r_0/2`
Chapter:
|
An electron with speed v0 << c moves in a circle of radius r0 in a uniform magnetic field. This electron is able to traverse a circular path as the magnetic force acting on the electron is perpendicular to both v0 and B, as shown in the figure. This force continuously deflects the particle sideways without changing its speed and the particle will move along a circle perpendicular to the field. The time required for one revolution of the electron is T0.
|
If v = 2v0, then the time required for one revolution of the electron (T0) will change to ______.
4T0
2T0
T0
`T_0/2`
Chapter:
|
An electron with speed v0 << c moves in a circle of radius r0 in a uniform magnetic field. This electron is able to traverse a circular path as the magnetic force acting on the electron is perpendicular to both v0 and B, as shown in the figure. This force continuously deflects the particle sideways without changing its speed and the particle will move along a circle perpendicular to the field. The time required for one revolution of the electron is T0.
|
A charged particle is projected in a magnetic field B = (2i + 4j) X 102 T. The acceleration of the particle is found to be a = (xi + 2j) m/s2. Find the value of x.
4 ms−2
−4 ms−2
−2 ms−2
2 ms−2
Chapter:
|
An electron with speed v0 << c moves in a circle of radius r0 in a uniform magnetic field. This electron is able to traverse a circular path as the magnetic force acting on the electron is perpendicular to both v0 and B, as shown in the figure. This force continuously deflects the particle sideways without changing its speed and the particle will move along a circle perpendicular to the field. The time required for one revolution of the electron is T0.
|
If the given electron has a velocity not perpendicular to B, then the trajectory of the electron is ______.
straight line
circular
helical
zig-zag
Chapter:
Advertisements
|
An electron with speed v0 << c moves in a circle of radius r0 in a uniform magnetic field. This electron is able to traverse a circular path as the magnetic force acting on the electron is perpendicular to both v0 and B, as shown in the figure. This force continuously deflects the particle sideways without changing its speed and the particle will move along a circle perpendicular to the field. The time required for one revolution of the electron is T0.
|
If this electron of charge (e) is moving parallel to a uniform magnetic field with constant velocity v, the force acting on the electron is ______.
Bev
`(Be)/v`
`B/(ev)`
Zero
Chapter:
| It is the phenomenon of the emission of electrons from a metallic surface when light of a suitable frequency is incident on it. The emitted electrons are called photoelectrons. Nearly all metals exhibit this effect with ultraviolet light but alkali metals like lithium, sodium, potassium, cesium, etc. show this effect even with visible light. It is an instantaneous process, i.e., photoelectrons are emitted as soon as the light is incident on the metal surface. The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is directly proportional to the intensity of the incident radiation. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted from a given metal surface is independent of the intensity of the incident light and depends only on the frequency of the incident light. For a given metal surface, there is a certain minimum value of the frequency of the incident light below which emission of photoelectrons does not occur. |
In a photoelectric experiment, plate current is plotted against anode potential.
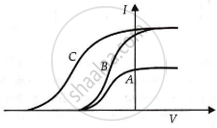
A and B will have the same intensities, while B and C will have different frequencies.
B and C will have different intensities, while A and B will have different frequencies.
A and B will have different intensities, while B and C will have equal frequencies.
B and C will have equal intensities, while A and B will have the same frequencies.
Chapter:
| It is the phenomenon of the emission of electrons from a metallic surface when light of a suitable frequency is incident on it. The emitted electrons are called photoelectrons. Nearly all metals exhibit this effect with ultraviolet light but alkali metals like lithium, sodium, potassium, cesium, etc. show this effect even with visible light. It is an instantaneous process, i.e., photoelectrons are emitted as soon as the light is incident on the metal surface. The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is directly proportional to the intensity of the incident radiation. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted from a given metal surface is independent of the intensity of the incident light and depends only on the frequency of the incident light. For a given metal surface, there is a certain minimum value of the frequency of the incident light below which emission of photoelectrons does not occur. |
Photoelectrons are emitted when a zinc plate is ______.
Heated
hammered
Irradiated by ultraviolet light
subjected to a high pressure
Chapter:
| It is the phenomenon of the emission of electrons from a metallic surface when light of a suitable frequency is incident on it. The emitted electrons are called photoelectrons. Nearly all metals exhibit this effect with ultraviolet light but alkali metals like lithium, sodium, potassium, cesium, etc. show this effect even with visible light. It is an instantaneous process, i.e., photoelectrons are emitted as soon as the light is incident on the metal surface. The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is directly proportional to the intensity of the incident radiation. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted from a given metal surface is independent of the intensity of the incident light and depends only on the frequency of the incident light. For a given metal surface, there is a certain minimum value of the frequency of the incident light below which emission of photoelectrons does not occur. |
The threshold frequency for the photoelectric effect on sodium corresponds to a wavelength of 500 nm. Its work function is about ______.
4 × 10−19 J
J
2 × 10−19 J
3 × 10−19 J
Chapter:
| It is the phenomenon of the emission of electrons from a metallic surface when light of a suitable frequency is incident on it. The emitted electrons are called photoelectrons. Nearly all metals exhibit this effect with ultraviolet light but alkali metals like lithium, sodium, potassium, cesium, etc. show this effect even with visible light. It is an instantaneous process, i.e., photoelectrons are emitted as soon as the light is incident on the metal surface. The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is directly proportional to the intensity of the incident radiation. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted from a given metal surface is independent of the intensity of the incident light and depends only on the frequency of the incident light. For a given metal surface, there is a certain minimum value of the frequency of the incident light below which emission of photoelectrons does not occur. |
The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted from a surface when photons of energy 6 eV fall on it is 4 eV. The stopping potential is ______.
2 V
4 V
6 V
10 V
Chapter:
| It is the phenomenon of the emission of electrons from a metallic surface when light of a suitable frequency is incident on it. The emitted electrons are called photoelectrons. Nearly all metals exhibit this effect with ultraviolet light but alkali metals like lithium, sodium, potassium, cesium, etc. show this effect even with visible light. It is an instantaneous process, i.e., photoelectrons are emitted as soon as the light is incident on the metal surface. The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is directly proportional to the intensity of the incident radiation. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted from a given metal surface is independent of the intensity of the incident light and depends only on the frequency of the incident light. For a given metal surface, there is a certain minimum value of the frequency of the incident light below which emission of photoelectrons does not occur. |
The minimum energy required to remove an electron from a substance is called its ______.
work function
kinetic energy
stopping potential
potential energy
Chapter:
Write two limitations of ohm’s law. Plot their I-V characteristics.
Chapter:
A heating element connected across a battery of 100 V having an internal resistance of 1 Ω draws an initial current of 10 A at room temperature 20.0°C, which settles after a few seconds to a steady value. What is the power consumed by the battery itself after the steady temperature of 320.0°C is attained? Temperature coefficient of resistance averaged over the temperature range involved is 3.70 × 10−4°C−1.
Chapter:
Using Kirchhoff's laws, obtain the equation of the balanced state in Wheatstone Bridge.
Chapter:
A wire of uniform cross-section and resistance of 12 ohm is bent in the shape of a circle as shown in the figure. A resistance of 10 ohms is connected to diametrically opposite ends C and D. A battery of emf 8V is connected between A and B. Determine the current flowing through arm AD.
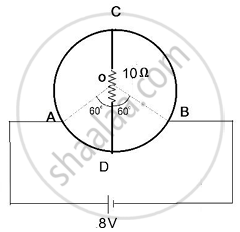
Chapter:
Explain briefly, with the help of a labelled diagram, the basic principle of the working of an a.c. generator. In an a.c. generator, a coil of N turns and area A is rotated at an angular velocity ω in a uniform magnetic field B. Derive an expression for the instantaneous value of the emf induced in coil. What is the source of energy generation in this device?
Chapter:
With the help of a diagram, explain the principle of a device which changes a low ac voltage into a high voltage. Deduce the expression for the ratio of secondary voltage to the primary voltage in terms of the ratio of the number of turns of primary and secondary winding. For an ideal transformer, obtain the ratio of primary and secondary currents in terms of the ratio of the voltages in the secondary and primary coils.
Chapter:
Write any two sources of the energy losses which occur in actual transformers.
Chapter:
A step-up transformer converts a low input voltage into a high output voltage. Does it violate the law of conservation of energy? Explain.
Chapter:
- A giant refracting telescope at an observatory has an objective lens of focal length 15 m. If an eyepiece of focal length 1.0 cm is used, what is the angular magnification of the telescope?
- If this telescope is used to view the moon, what is the diameter of the image of the moon formed by the objective lens? The diameter of the moon is 3.48 × 106 m, and the radius of lunar orbit is 3.8 × 108 m.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A compound microscope consists of an objective lens of focal length 2.0 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 6.25 cm separated by a distance of 15 cm. How far from the objective should an object be placed in order to obtain the final image at
- the least distance of distinct vision (25 cm), and
- infinity?
What is the magnifying power of the microscope in each case?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2024 - 2025
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2025 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.