Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Ram is a student of class X in a village school. His uncle gifted him a bicycle with a dynamo fitted in it. He was very excited to get it. While cycling during night, he could light the bulb and see the objects on the road. He, however, did not know how this device works. he asked this question to his teacher. The teacher considered it an opportunity to explain the working to the whole class.
Answer the following questions:
(a) State the principle and working of a dynamo.
(b) Write two values each displayed by Ram and his school teacher.
उत्तर
(a) The underlying principle in the working of a dynamo is that changing magnetic flux in a conductor induces emf. A dynamo includes a coil attached to a small turbine fitted with a plastic cap. The coil is placed in a magnetic field. When the plastic cap comes in contact with moving tyres of the bicycle, the coil placed between the poles of a magnet rotates, thus the flux through the coil changes continuously. This induces a current in the coil which is connected to a bulb which lights up. As long as the bicycle is moving, the coil keeps on rotating, and hence, the flux keeps on changing. At a steady rate, we get a steady current and hence a light of steady intensity.
(b) The qualities shown by the teacher are: helpful and responsible as a teacher, and knowledgeable. The qualities shown by Ram are inquisitive and observing.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A square loop MNOP of side 20 cm is placed horizontally in a uniform magnetic field acting vertically downwards as shown in the figure. The loop is pulled with a constant velocity of 20 cm s−1 till it goes out of the field.
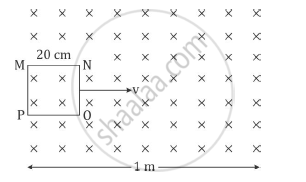
(i) Depict the direction of the induced current in the loop as it goes out of the field. For how long would the current in the loop persist?
(ii) Plot a graph showing the variation of magnetic flux and induced emf as a function of time.
A pair of adjacent coils has a mutual inductance of 1.5 H. If the current in one coil changes from 0 to 20 A in 0.5 s, what is the change of flux linkage with the other coil?
Find magnetic flux density at a point on the axis of a long solenoid having 5000 tums/m when it carrying a current of 2 A.
The magnetic flux linked with a coil of N turns of area of cross-section A held with its plane parallel to the field B is ______.
Two inductors of inductance L each are connected in series with the opposite? magnetic fluxes. The resultant inductance is ______.
A square of side L meters lies in the x-y plane in a region, where the magnetic field is given by `B = Bo(2hati + 3hatj + 4hatk)`T, where B0 is constant. The magnitude of flux passing through the square is ______.
A coil is placed in a time varying magnetic field. If the number of turns in the coil were to be halved and the radius of wire doubled, the electrical power dissipated due to the current induced in the coil would be: (Assume the coil to be short circuited.)
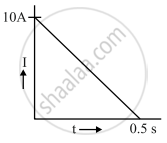
In a coil of resistance 100 Ω a current is induced by changing the magnetic flux through it. The variation of current with time is shown in the figure. The magnitude of change in flux through the coil is ______.
A circular coil has radius ‘r', number of turns ‘N’ and carries a current ‘I’. Magnetic flux density ‘B’ at its centre is ______.
