Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A pair of adjacent coils has a mutual inductance of 1.5 H. If the current in one coil changes from 0 to 20 A in 0.5 s, what is the change of flux linkage with the other coil?
उत्तर
We are interested in the flux change associated with coil 2 as the current in coil 1 changes from 0 to 20 A.
∅2 = MI1
and Δ∅2 = MΔI1
Δ∅2 = 1.5 [20 – 0]
or Δ∅2 = 30 Wb
Here, the current is increasing, so the change in flux density will oppose the increase in current.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a schematic sketch of an ac generator describing its basic elements. State briefly its working principle. Show a plot of variation of
(i) Magnetic flux and
(ii) Alternating emf versus time generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field.
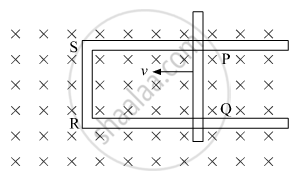
Figure shows a rectangular loop conducting PQRS in which the arm PQ is free to move. A uniform magnetic field acts in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the loop. Arm PQ is moved with a velocity v towards the arm Rs. Assuming that the arms QR, RS and SP have negligible resistances and the moving arm PQ has the resistance r, obtain the expression for (i) the current in the loop (ii) the force and (iii) the power required to move the arm PQ.
How does the mutual inductance of a pair of coils change when
(i) distance between the coils is increased and
(ii) number of turns in the coils is increased?
An inductor is connected to a battery through a switch. Explain why the emf induced in the inductor is much larger when the switch is opened as compared to the emf induced when the switch is closed.
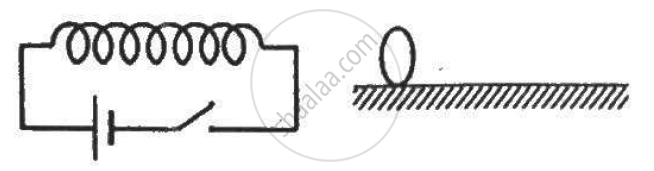
Figure shows a horizontal solenoid connected to a battery and a switch. A copper ring is placed on a frictionless track, the axis of the ring being along the axis of the solenoid. As the switch is closed, the ring will __________ .
Find magnetic flux density at a point on the axis of a long solenoid having 5000 tums/m when it carrying a current of 2 A.
Answer the following question.
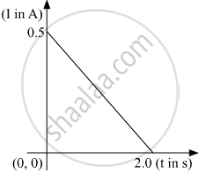
When a conducting loop of resistance 10 Ω and area 10 cm2 is removed from an external magnetic field acting normally, the variation of induced current-I in the loop with time t is as shown in the figure.
Find the
(a) total charge passed through the loop.
(b) change in magnetic flux through the loop
(c) magnitude of the field applied
The magnetic flux linked with the coil (in Weber) is given by the equation- Փ = 5t2 + 3t + 16. The induced EMF in the coil at time, t = 4 will be ______.
The unit of magnetic flux in SI is ______
A square of side L meters lies in the x-y plane in a region, where the magnetic field is given by `B = Bo(2hati + 3hatj + 4hatk)`T, where B0 is constant. The magnitude of flux passing through the square is ______.
A loop, made of straight edges has six corners at A(0, 0, 0), B(L, O, 0) C(L, L, 0), D(0, L, 0) E(0, L, L) and F(0, 0, L). A magnetic field `B = B_o(hati + hatk)`T is present in the region. The flux passing through the loop ABCDEFA (in that order) is ______.
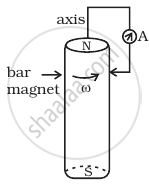
A cylindrical bar magnet is rotated about its axis (Figure). A wire is connected from the axis and is made to touch the cylindrical surface through a contact. Then
A coil is placed in a time varying magnetic field. If the number of turns in the coil were to be halved and the radius of wire doubled, the electrical power dissipated due to the current induced in the coil would be: (Assume the coil to be short circuited.)
The Figure below shows an infinitely long metallic wire YY' which is carrying a current I'.
P is a point at a perpendicular distance r from it.
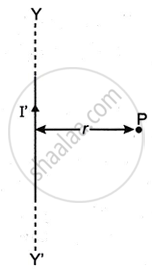
- What is the direction of magnetic flux density B of the magnetic field at the point P?
- What is the magnitude of magnetic flux density B of the magnetic field at the point P?
- Another metallic wire MN having length l and carrying a current I is now kept at point P. If the two wires are in vacuum and parallel to each other, how much force acts on the wire MN due to the current I' flowing in the wire YY'?
