Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A loop, made of straight edges has six corners at A(0, 0, 0), B(L, O, 0) C(L, L, 0), D(0, L, 0) E(0, L, L) and F(0, 0, L). A magnetic field `B = B_o(hati + hatk)`T is present in the region. The flux passing through the loop ABCDEFA (in that order) is ______.
पर्याय
`B_o L^2 Wb`
`2B_o L^2 Wb`
`sqrt(2) B_o L^2 Wb`
`4B_o L^2 Wb`
उत्तर
A loop, made of straight edges has six corners at A(0, 0, 0), B(L, O, 0) C(L, L, 0), D(0, L, 0) E(0, L, L) and F(0, 0, L). A magnetic field `B = B_o(hati + hatk)`T is present in the region. The flux passing through the loop ABCDEFA (in that order) is `underline(2B_o L^2 Wb`).
Explanation:
In this problem first we have to analyse area vector, loop ABCDA lies in x-y plane whose area vector `vecA_1 = L^2 hatk` whereas loop ADEFA lies in y-z plane whose area vector `vecA_2 = L^2 hati`
And the magnetic flux is `phi_m = vecB * vecA`
`vecA = vecA_1 + vecA_2 = (L^2 hatk + L^2 hati)`
And `vecB = B_0(hati + hatk)`
Now, `phi_m = vecB * vecA = B_0(hati + hatk)*(L^2 hatk + L^2hati)`
= `2B_0L^2 Wb`

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Ram is a student of class X in a village school. His uncle gifted him a bicycle with a dynamo fitted in it. He was very excited to get it. While cycling during night, he could light the bulb and see the objects on the road. He, however, did not know how this device works. he asked this question to his teacher. The teacher considered it an opportunity to explain the working to the whole class.
Answer the following questions:
(a) State the principle and working of a dynamo.
(b) Write two values each displayed by Ram and his school teacher.
Draw a schematic sketch of an ac generator describing its basic elements. State briefly its working principle. Show a plot of variation of
(i) Magnetic flux and
(ii) Alternating emf versus time generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field.
An inductor is connected to a battery through a switch. Explain why the emf induced in the inductor is much larger when the switch is opened as compared to the emf induced when the switch is closed.
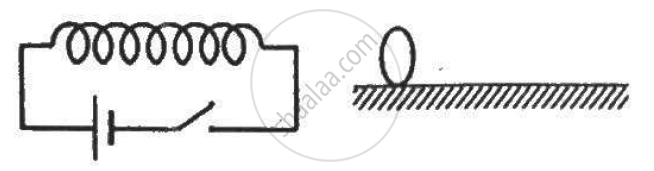
Figure shows a horizontal solenoid connected to a battery and a switch. A copper ring is placed on a frictionless track, the axis of the ring being along the axis of the solenoid. As the switch is closed, the ring will __________ .
Find magnetic flux density at a point on the axis of a long solenoid having 5000 tums/m when it carrying a current of 2 A.
The magnetic flux linked with a coil of N turns of area of cross-section A held with its plane parallel to the field B is ______.
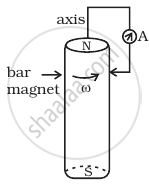
A cylindrical bar magnet is rotated about its axis (Figure). A wire is connected from the axis and is made to touch the cylindrical surface through a contact. Then
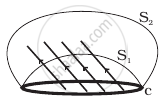
Consider a closed loop C in a magnetic field (Figure). The flux passing through the loop is defined by choosing a surface whose edge coincides with the loop and using the formula φ = B1.dA1 + B2.dA2 +... Now if we chose two different surfaces S1 and S2 having C as their edge, would we get the same answer for flux. Jusity your answer.
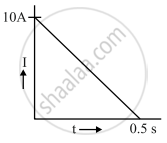
In a coil of resistance 100 Ω a current is induced by changing the magnetic flux through it. The variation of current with time is shown in the figure. The magnitude of change in flux through the coil is ______.