Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A loop, made of straight edges has six corners at A(0, 0, 0), B(L, O, 0) C(L, L, 0), D(0, L, 0) E(0, L, L) and F(0, 0, L). A magnetic field `B = B_o(hati + hatk)`T is present in the region. The flux passing through the loop ABCDEFA (in that order) is ______.
Options
`B_o L^2 Wb`
`2B_o L^2 Wb`
`sqrt(2) B_o L^2 Wb`
`4B_o L^2 Wb`
Solution
A loop, made of straight edges has six corners at A(0, 0, 0), B(L, O, 0) C(L, L, 0), D(0, L, 0) E(0, L, L) and F(0, 0, L). A magnetic field `B = B_o(hati + hatk)`T is present in the region. The flux passing through the loop ABCDEFA (in that order) is `underline(2B_o L^2 Wb`).
Explanation:
In this problem first we have to analyse area vector, loop ABCDA lies in x-y plane whose area vector `vecA_1 = L^2 hatk` whereas loop ADEFA lies in y-z plane whose area vector `vecA_2 = L^2 hati`
And the magnetic flux is `phi_m = vecB * vecA`
`vecA = vecA_1 + vecA_2 = (L^2 hatk + L^2 hati)`
And `vecB = B_0(hati + hatk)`
Now, `phi_m = vecB * vecA = B_0(hati + hatk)*(L^2 hatk + L^2hati)`
= `2B_0L^2 Wb`

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Ram is a student of class X in a village school. His uncle gifted him a bicycle with a dynamo fitted in it. He was very excited to get it. While cycling during night, he could light the bulb and see the objects on the road. He, however, did not know how this device works. he asked this question to his teacher. The teacher considered it an opportunity to explain the working to the whole class.
Answer the following questions:
(a) State the principle and working of a dynamo.
(b) Write two values each displayed by Ram and his school teacher.
A pair of adjacent coils has a mutual inductance of 1.5 H. If the current in one coil changes from 0 to 20 A in 0.5 s, what is the change of flux linkage with the other coil?
How does the mutual inductance of a pair of coils change when
(i) distance between the coils is increased and
(ii) number of turns in the coils is increased?
Calculate magnetic flux density of the magnetic field at the centre of a circular coil of 50 turns, having a radius of 0.5m and carrying a current of 5 A.
Whenever the magnetic flux linked with an electric circuit changes, an emf is induced in the circuit. This is called ______.
The magnetic flux linked with the coil (in Weber) is given by the equation- Փ = 5t2 + 3t + 16. The induced EMF in the coil at time, t = 4 will be ______.
A square of side L meters lies in the x-y plane in a region, where the magnetic field is given by `B = Bo(2hati + 3hatj + 4hatk)`T, where B0 is constant. The magnitude of flux passing through the square is ______.
A coil is placed in a time varying magnetic field. If the number of turns in the coil were to be halved and the radius of wire doubled, the electrical power dissipated due to the current induced in the coil would be: (Assume the coil to be short circuited.)
The Figure below shows an infinitely long metallic wire YY' which is carrying a current I'.
P is a point at a perpendicular distance r from it.
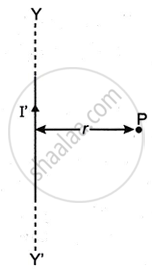
- What is the direction of magnetic flux density B of the magnetic field at the point P?
- What is the magnitude of magnetic flux density B of the magnetic field at the point P?
- Another metallic wire MN having length l and carrying a current I is now kept at point P. If the two wires are in vacuum and parallel to each other, how much force acts on the wire MN due to the current I' flowing in the wire YY'?
