Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the relation between work, charge and potential difference for an electric circuit.
उत्तर
The relation between work (W), charge (Q) and potential difference (V):
The work required to be done (W) to move a positive charge Q, between two points in a circuit having potential difference V, is QV. That is,
W = QV
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
<p> Define the unit of electric current (or Define ampere).
An electric bulb of resistance 20 Ω and a resistance wire of 4 Ω are connected in series with a 6 V battery.
Draw the circuit diagram, and calculate:
(a) total resistance of the circuit.
(b) current through the circuit.
(c) potential difference across the electric bulb.
(d) potential difference across the resistance wire.
Draw a circuit diagram showing two lamps, one cell and a switch connected in series.
How can you change the brightness of the lamp?
A wire of length 5 m has a resistance of 2.0 Ω calculate:
(a) the resistance of wire of length 1 m
(b) the equivalent resistance if two such wires each of length 2 m are joined in parallel.
(c) the resistance of 1 m length of wire of same material but of half diameter.
Define the following:
Electromotive force
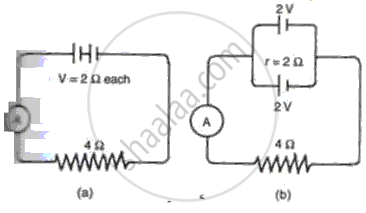
Two cells each having an e.m.f. of 2 V and an internal resistance of 2Ω are
connected (a) In series, and ( b) In para 1le l as shown in fig. . What is the
current flowing through the cir cu it in each_ case?
Tick (✓) the correct choice among the following :
Which of the following changes would enable a millimeter to be used as a
direct current ammeter reading upto 1 A?
Water : pipe :: Electric current : ______.
Match the items in column-I to the items in column-II:
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
| (i) | electric current | (a) | volt |
| (ii) | potential difference | (b) | ohm meter |
| (iii) | specific resistance | (c) | watt |
| (iv) | electrical power | (d) | joule |
| (v) | electrical energy | (e) | ampere |
