Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the impact of "Excess Demand" under the Keynesian theory on employment, in an economy.
उत्तर
Excess demand refers to a situation where the aggregate demand for output is more than the full employment level of output.
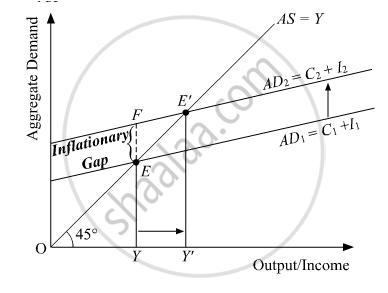
Due to the excess of aggregate demand, there exists a difference (or gap) between the actual level of aggregate demand and full employment level of demand. This difference is termed as an inflationary gap. This gap measures the amount of surplus in the level of aggregate demand. Graphically, it is represented by the vertical distance between the actual level of aggregate demand (ADE) and the full employment level of output (ADF). In the figure, EY denotes the aggregate demand at the full employment level of output and FY denotes the actual aggregate demand. The vertical distance between these two represents the inflationary gap. That is,
FY – EY = FE (Inflationary Gap)
Let us understand the situation of excess demand and the concept of the inflationary gap with the help of the following figure.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the role of taxation in reducing excess demand.
What is a fiscal measure of correcting deficient demand?
Supply creates its own Demand. Who gave this law?
If income equilibrium level in the economy is determined at the level before full employment, it is known as the state of ______
In Keynesian economics, the state of Deficit Demand is called as ______
Deflationary Gap shows the measurement of ______
Which one is the reason for appearing Deficit Demand condition?
Which of the following is true?
Give the meaning of deficient demand.
If S > I, it will lead to ______.
