Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose the spheres A and B in Exercise 1.12 have identical sizes. A third sphere of the same size but uncharged is brought in contact with the first, then brought in contact with the second, and finally removed from both. What is the new force of repulsion between A and B?
उत्तर
Distance between the spheres, A and B, r = 0.5 m
Initially, the charge on each sphere, q = 6.5 × 10−7 C
When sphere A is touched with an uncharged sphere C, `"q"/2` amount of charge from A will transfer to sphere C. Hence, the charge on each of the spheres, A and C, is `"q"/2`.
When sphere C with charge `"q"/2` is brought in contact with sphere B with charge q, total charges on the system will divide into two equal halves given as,
`("q"/2 + "q")/2 = (3"q")/4`
Each sphere will share each half. Hence, the charge on each of the spheres, C and B, is `(3"q")/4`.
Force of repulsion between sphere A having charge `"q"/2` and sphere B having charge
`(3"q")/4 = ("q"/2 xx (3"q")/4)/(4piin_0"r"^2) = (3"q"^2)/(8 xx 4piin_9"r"^2)`
= `9 xx 10^9 xx (3 xx (6.5 xx 10^-7)^2)/(8 xx (0.5)^2)`
= `5.703 xx 10^-3` N
Therefore, the force of attraction between the two spheres is 5.703 × 10−3 N.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the force of repulsion if each sphere is charged double the above amount, and the distance between them is halved?
(a) Consider an arbitrary electrostatic field configuration. A small test charge is placed at a null point (i.e., where E = 0) of the configuration. Show that the equilibrium of the test charge is necessarily unstable.
(b) Verify this result for the simple configuration of two charges of the same magnitude and sign placed a certain distance apart.
In charging by Induction, a metallic object is charged ______.
A point charge + q is placed at a distance d from an isolated conducting plane. The field at a point P on the other side of the plane is ______.
Two small balls having the same mass and charge and located on the same vertical at heights h1 and h2 are thrown in the same direction along the horizontal at the same velocity v. The first ball touches the ground at a distance l from the initial vertical. At what height H2 will the second ball be at this instant ? The air drag and the effect of the charges induced on the ground should be neglected.
A positive charge Q is uniformly distributed along a circular ring of radius R. A small test charge q is placed at the centre of the ring (figure). Then
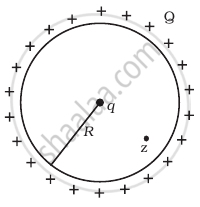
- If q > 0 and is displaced away from the centre in the plane of the ring, it will be pushed back towards the centre.
- If q < 0 and is displaced away from the centre in the plane of the ring, it will never return to the centre and will continue moving till it hits the ring.
- If q < 0, it will perform SHM for small displacement along the axis.
- q at the centre of the ring is in an unstable equilibrium within the plane of the ring for q > 0.
