Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The following figure shows a metal rod PQ mounted on an insulated stand. The cap of an uncharged electroscope touches one end Q of the metal rod. A negatively charged ebonite rod is brought near the other end P of the metal rod.
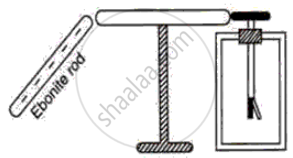
(a) What charge does the end P have?
(b) What charge does the end Q have?
(c) What charge does the cap of the electroscope have?
(d) What charge does the gold leaf have?
(e) Will the leaf diverge or collapse? Give reason.
(f) If the electroscope is now earthed, what charge does the metal rod have?
उत्तर
(a) P will have a positive charge
(b) Q will have no charge.
(c) The Cap of the electroscope will have no charge.
(d) The gold leaf will have a negative charge.
(e) The leaf will diverse because like charges repel each other
(f) If electroscope is earthed then the metal rod will have a positive charge.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
n electrons flow through a cross section of a conductor in time t. If charge on an electron is e, then write an expression for the current in the conductor.
Define the term potential difference.
A bulb draws current 1.5 A at 6.0 V. Find the resistance of filament of bulb while glowing.
There is a positively charged sphere A and negatively charged sphere B, such that they are brought in electrical contact by a copper wire.
In which direction electronic current flows?
State and define the SI unit of electric current.
Calculate the total number of electrons flowing through a circuit in 20 mins and 40 s, if a current of 40 μA flows through the circuit.
[1 e– = 1.6 × 10-19 C]
4 × 1020 electrons flow through a circuit in 10 hours. Calculate magnitude of current. [1 e- = 1.6 × 10-19 C]
Draw a diagram showing two bulbs connected in series to a dry cell.
