Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the term potential difference.
उत्तर
The amount of work done in moving a unit positive charge from one point to another point in an electric field is called the potential difference.
संबंधित प्रश्न
n electrons flow through a cross section of a conductor in time t. If charge on an electron is e, then write an expression for the current in the conductor.
What is the function of a key (or switch) in an electric circuit?
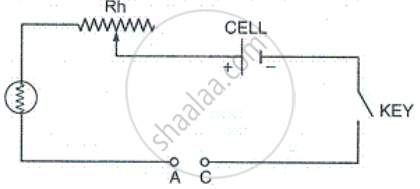
(a) Complete the circuit given in Fig. by inserting between the terminals A and C. an ammeter.
(b) In the diagram, mark the polarity at the terminals of ammeter and indicate clearly the direction of flow of current in the circuit when the circuit is complete.
(c) Name and state the purpose of Rh in the circuit.
State whether the resistance of filament of a bulb will decrease, remain unchanged or increase when it glows.
There is a positively charged sphere A and negatively charged sphere B, such that they are brought in electrical contact by a copper wire.
Which sphere is at higher potential before electrical contact on the basis of convention?
How many electrons constitute one unit electric charge in SI system?
How is potential difference related to work done and quantity of charge?
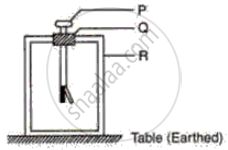
The following Figure represents a negatively charged gold Ieaf electroscope. Label the parts, P, Q, and R and the estate whether each is an insulator or a conductor. Also, indicate the distribution of charges on the system in the diagram.
The following figure shows a metal rod PQ mounted on an insulated stand. The cap of an uncharged electroscope touches one end Q of the metal rod. A negatively charged ebonite rod is brought near the other end P of the metal rod.
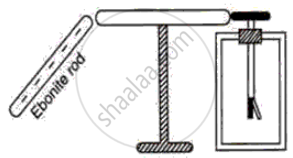
(a) What charge does the end P have?
(b) What charge does the end Q have?
(c) What charge does the cap of the electroscope have?
(d) What charge does the gold leaf have?
(e) Will the leaf diverge or collapse? Give reason.
(f) If the electroscope is now earthed, what charge does the metal rod have?
Label the different parts A, B, C, D, E, and F. State the functions of each part. Show in the diagram the direction of flow of current.
