Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 9 - Current Electricity Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 9 - Current Electricity - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-physics-english-class-9-icse_6:8a0c4572dea049a29e575abe2d9ca662.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 9: Current Electricity
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 9 of CISCE Selina for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 9 Current Electricity Exercise 9 (A) [Page 193]
Name one D.C. source and one A.C. source.
Distinguish between D.C. and A.C.
What is an electric cell?
What transformation of energy takes place when current is drawn from a cell?
Name the constituents of a cell.
State the two kinds of cell. Give one example of each.
What is a primary cell? Name two such cells.
What is a secondary cell? Name one such cell.
State three differences between the primary and secondary cells.
What do you understand by the term current? State and define its S.I. unit.
How much is the charge on an electron?
n electrons flow through a cross section of a conductor in time t. If charge on an electron is e, then write an expression for the current in the conductor.
Name the instrument used to control the current in an electric circuit.
In the electric circuit shown in Figure, label the parts A, B, C, D, E, and F. State the function of each part. Show in the diagram the direction of flow of current.

What is the function of a key (or switch) in an electric circuit?
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit : key
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit :
cell
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit :
rheostat
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit :
ammeter
Write symbol and state function of following component in an electric circuit :
voltmeter
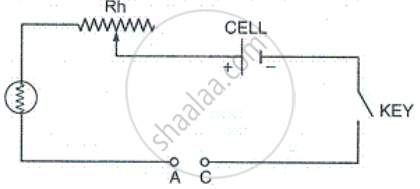
(a) Complete the circuit given in Fig. by inserting between the terminals A and C. an ammeter.
(b) In the diagram, mark the polarity at the terminals of ammeter and indicate clearly the direction of flow of current in the circuit when the circuit is complete.
(c) Name and state the purpose of Rh in the circuit.
What are conductors and insulators of electricity? Give two examples of each.
Select conductors of electricity from the following: Copper wire, silk thread, pure water, acidulated water, human body, glass, mercury.
State two differences between a conductor and an insulator of electricity.
Distinguish between a closed circuit and an open circuit, with the use of suitable labelled diagrams.
Write the condition required for a circuit to be a closed circuit.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 9 Current Electricity Exercise 9 (A) [Page 193]
A cell is used to :
measure current in a circuit
provide current in a circuit
check current in a circuit
prevent current in a circuit.
The unit of current is :
ampere
volt
ohm
coulomb
The insulator of electricity is :
Copper
Acidulated water
Human body
Silk
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 9 Current Electricity Exercise 9 (A) [Page 194]
A charge 0.5 C passes through a cross section of a conductor in 5 s . Find the current .
A current of 1.5 A flows through a conductor for 2.0 s . What amount of charge passes through the conductor ?
When starter motor of a car is switched on for 0.8 s . a charge 24 C passes through the coil of the motor . Calculate the current in the coil .
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 9 Current Electricity Exercise 9 (B) [Page 198]
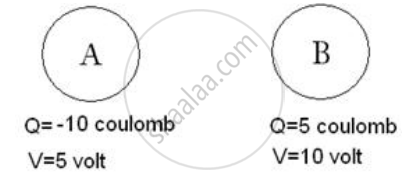
Figure. below shows two conductors A and B. Their charges and potentials are given in diagram. State the direction of (i) flow of electrons and (ii) flow of current, when both the conductors are joined by a metal wire.
How is the direction of flow of current between the two charged conductors determined by their potentials?
Explain the concept of electric potential difference in terms of work done in transferring the charge.
Define the term potential difference.
State and define the S.I. unit of potential difference.
'The potential difference between two conductors is 1 volt'. Explain the meaning of this statement.
What do you understand by the term resistance?
Explain why does a metal wire when connected to a cell offer resistance to the flow of current.
State and define the S.I. unit of resistance.
State Ohm's law.
How are the potential difference (V), current (l) and resistance (R) related?
'The resistance of a wire is 1 ohm'. Explain the meaning of this statement.
How is the current flowing in a conductor changed if the resistance of conductor is doubled keeping the potential difference across it the same?
State three factors on which the resistance of a wire depends. Explain how the resistance depends on the factors stated by you.
How is the resistance of a wire affected if its (a) length is doubled, (b) radius is doubled?
State whether the resistance of filament of a bulb will decrease, remain unchanged or increase when it glows.
Name the physical quantity of which the unit is volt
Name the physical quantity of which the unit is coulomb
Name the physical quantity of which the unit is ohm
Name the physical quantitiy of which the unit is ampere
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 9 Current Electricity Exercise 9 (B) [Page 198]
Current in a circuit flows :
In direction from high potential to low potential
In direction from low potential to high potential
In direction of flow of electrons
In any direction.
The unit of potential difference is :
ampere
volt
ohm
coulomb
On increasing the resistance in a circuit, the current in it :
Decreases
Increases
Remains unchanged
Nothing can be said.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 9 Current Electricity Exercise 9 (B) [Page 198]
In transferring 1.5 C charge through a wire, 9 J of work is needed. Find the potential difference across the wire.
A cell of potential difference 12 V is connected to a bulb. The resistance of filament of bulb when it glows is 24Ω. Find the current drawn from the cell.
A bulb draws current 1.5 A at 6.0 V. Find the resistance of filament of bulb while glowing.
A current 0.2 A flows in a wire of resistance 15Ω. Find the potential difference across the ends of the wire.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 9 Current Electricity Exercise 9 (C) [Page 199]
What is meant by the efficient use of energy?
State two ways to save the energy.
How does the proper insulation of home save energy?
Which of the following device is most efficient for the lighting purpose?
LED, CFL, fluorescent tube light, Electric bulb.
Give an example to explain that the use of modem eco-friendly technology is more efficient and less polluting.
Describe three ways for the efficient use of energy.
What social initiatives must be taken for the sensitive use of energy?
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 9 Current Electricity Exercise 9 (C) [Page 199]
The most non-polluting and efficient lighting device is :
CFL
LED
Fluorescent light
Electric bulb
IEA is the short form of :
Indian Energy Association
Indian Eco Academy
International Energy Agency
International Eco Academy
Solutions for 9: Current Electricity
![Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 9 - Current Electricity Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 9 - Current Electricity - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-physics-english-class-9-icse_6:8a0c4572dea049a29e575abe2d9ca662.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 9 - Current Electricity
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE 9 (Current Electricity) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 9 Current Electricity are Electric cell, Symbols and Functions of Various Components of an Electric Circuits, Direction of the Electric Current - Conventional and Electronic Flow, Conservation of Electrical Energy, Electric Current, Electric Circuit, Types of Circuits: Simple Circuit, Conductors and Insulators, Flow of Charges (Electrons) Between Conductor, Potential and Potential Difference, Resistance (R), Ohm's Law (V = IR), Social Initiatives for Energy, Factors Affecting the Resistance of a Conductor.
Using Selina Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE solutions Current Electricity exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 9, Current Electricity Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
