Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the electric circuit shown in Figure, label the parts A, B, C, D, E, and F. State the function of each part. Show in the diagram the direction of flow of current.

उत्तर
A: Ammeter - It measures the current flowing through the circuit.
B: Cell - It acts as a source of direct current for the circuit.
C: Key - It is used to put the current on and off in the circuit.
D: Load - It is an appliance connected in a circuit. It may just be a resistance (e.g., bulb) or a combination of different electrical components.
E: Voltmeter - It is used to measure the potential difference between two points of a circuit.
F: Rheostat - It is used to control the current in the circuit.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State three differences between the primary and secondary cells.
Define electric potential in terms of energy spent.
Why does the filament of an electric bulb in an electric circuit get white-hot, but not the connecting wires?
Draw a diagram showing two bulbs connected in parallel to a dry cell.
The following figure shows a metal rod PQ mounted on an insulated stand. The cap of an uncharged electroscope touches one end Q of the metal rod. A negatively charged ebonite rod is brought near the other end P of the metal rod.
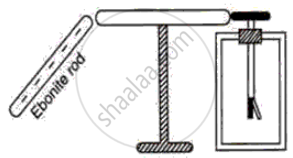
(a) What charge does the end P have?
(b) What charge does the end Q have?
(c) What charge does the cap of the electroscope have?
(d) What charge does the gold leaf have?
(e) Will the leaf diverge or collapse? Give reason.
(f) If the electroscope is now earthed, what charge does the metal rod have?
'The resistance of a wire is 2 ohm'. Explain the meaning of this statement.
Compare the brightness of two 60 watt bulbs.
When they are connected in parallel.
Explain giving scientific reasons.
