Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The conversion of an alkyl halide into an alkene by alcoholic KOH is classified as ______.
पर्याय
a substitution reaction
an addition reaction
a dehydrohalogenation reaction
a dehydration reaction
उत्तर
The conversion of an alkyl halide into an alkene by alcoholic KOH is classified as a dehydrohalogenation reaction.
Explanation:
When an alkyl halide is treated with an alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH), hydrogen halide is removed. It leads to the production of alkene. This is an example of a dehydrohalogenation (β-elimination) reaction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Identify the product ‘D’ in the following sequence of reactions:
\[\ce{H3C - CH2 - CH2 - Cl \underset{KOH}{\overset{Alc}{->}} 'B' \overset{HBr}{->} 'C' \underset{Elther}{\overset{Na}{->}}'D'}\]
State and explain Markownikoff's rule with suitable example
Write the main products when n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH.
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halide with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene:
2, 2, 3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{(CH3)3CBr + KOH ->[ethanol][heat]}\]
How the following conversion can be carried out?
1-Bromopropane to 2-bromopropane
Observe the following compounds and answer the questions given below.
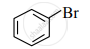
(I)
\[\ce{\underset{\text{(II)}}{CH3 - CH2 - Br}}\]
- Identify the type of halides.
- Explain the nature of the C – Br bond in both of these halides.
- Which of these compounds will undergo aqueous alkaline hydrolysis readily? Write the reaction in support of your answer.
Deamination of meso- di bromobutane gives mainly:-
Identify the major product formed when 2-cyclohexylchloroethane undergoes a dehydrohalogenation reaction. Name the reagent which is used to carry out the reaction.
Elimination of bromine from 2-bromobutane results in the formation of ______.
