Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Observe the following compounds and answer the questions given below.
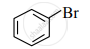
(I)
\[\ce{\underset{\text{(II)}}{CH3 - CH2 - Br}}\]
- Identify the type of halides.
- Explain the nature of the C – Br bond in both of these halides.
- Which of these compounds will undergo aqueous alkaline hydrolysis readily? Write the reaction in support of your answer.
उत्तर
- I - Haloarene/Aryl halide
II - Haloalkane/Alkyl halide - 1. In compound (I), the halogen atom (–Br) is directly bonded to the sp2 hybridized carbon atom of the aromatic ring. One of the lone pairs of electrons on the Br atom is in conjugation with π-electrons of the ring.
Due to resonance, the C – Br bond acquires partial double bond character. As a result, the C – Br bond in compound (I) is stronger and shorter than compound (II).
2. In compound (II), the halogen atom (–Br) is bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon which is a part of the saturated carbon skeleton. The C – Br bond in compound (I) is a polar covalent bond as –Br is more electronegative than carbon. - Compound (II) will undergo aqueous alkaline hydrolysis readily. Aqueous alkaline hydrolysis of ethyl bromide can be given as,
\[\ce{\underset{\text{Ethyl bromide}}{CH3CH2 - Br} + \underset{\text{Nucleophile}}{OH-} -> \underset{\text{Ethanol}}{CH3CH2 - OH} + \underset{\text{Bromide ion}}{Br-}}\]
संबंधित प्रश्न
Identify the product ‘D’ in the following sequence of reactions:
\[\ce{H3C - CH2 - CH2 - Cl \underset{KOH}{\overset{Alc}{->}} 'B' \overset{HBr}{->} 'C' \underset{Elther}{\overset{Na}{->}}'D'}\]
Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’ in the following reaction :
\[\ce{CH3 - CH = CH2 ->[HBr]'A' ->[alc.KOH]'B'}\]
State and explain Markownikoff's rule with suitable example
How do you convert: 2-bromobutane to but-2-ene
Write the main products when n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH.
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halide with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene:
1-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexane
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halide with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene:
2-Chloro-2-methylbutane
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halide with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene:
2, 2, 3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane
How will you bring about the following conversion?
But-1-ene to but-2-ene
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{(CH3)3CBr + KOH ->[ethanol][heat]}\]
How the following conversion can be carried out?
1-Bromopropane to 2-bromopropane
How the following conversion can be carried out?
2-Chloropropane to 1-propanol
How the following conversion can be carried out?
2-Bromopropane to 1-bromopropane
Draw a neat, labelled energy profile diagram for SN1 reaction mechanism.
What are racemates?

'A' is:
Deamination of meso- di bromobutane gives mainly:-
Identify the major product formed when 2-cyclohexylchloroethane undergoes a dehydrohalogenation reaction. Name the reagent which is used to carry out the reaction.
Elimination of bromine from 2-bromobutane results in the formation of ______.
The conversion of an alkyl halide into an alkene by alcoholic KOH is classified as ______.
Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
\[\ce{CH3 C(CI) (C2H5)CH2CH3 }\]
