Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The correct sequencing of angle of incidence, angle of emergence, angle of refraction and lateral displacement shown in the following diagram by digits 1, 2, 3 and 4 is:
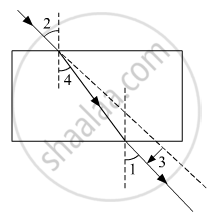
(a) 2, 4, 1, 3
(b) 2, 1, 4, 3
(c) 1, 2, 4, 3
(d) 2, 1, 3, 4
उत्तर
Angle 2 is angle of incidence. As, it is formed between the incident ray and the normal.
Angle 1 is angle of emergence. As, it is formed between the emergent ray with normal.
Angle 4 is angle of refraction. As, it is formed between the refracted ray and the normal.
3 shows the lateral displacement.
Hence, the correct answer is 2, 1, 4, 3
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The phenomenon that causes the twinkling of stars is refraction of light.
Name two effects produced by the atmospheric refraction.
State whether the following statement is true or false:
The planets twinkle at night due to atmospheric refraction of light.
The stars twinkle but the planets do not twinkle at night because:
(a) the stars are small but the planets are large
(b) the stars are very large but planets are small
(c) the stars are much nearer but planets are far off
(d) the stars are far off but planets are nearer to earth
As light from a far off star comes down towards the earth:
(a) it bends away from the normal
(b) it bends towards the normal
(c) it does not bend at all
(d) it is reflected back
A student claims that because of atmospheric refraction, the sun can be seen after it has set, and the day is, therefore, longer than if the earth had no atmosphere.
What does the student mean by saying that the sun can be seen after it has set?
State two effects produced by the scattering of light by the atmosphere.
What causes the scattering of blue component of sunlight in the atmosphere?
Assertion: Sky appears blue in the day time.
Reason: White light is composed of seven colours.
Explain the refraction of light through a triangular glass prism using a labelled ray diagram. Hence define the angle of deviation.
