Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The correct sequencing of angle of incidence, angle of emergence, angle of refraction and lateral displacement shown in the following diagram by digits 1, 2, 3 and 4 is:
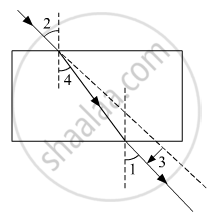
(a) 2, 4, 1, 3
(b) 2, 1, 4, 3
(c) 1, 2, 4, 3
(d) 2, 1, 3, 4
Solution
Angle 2 is angle of incidence. As, it is formed between the incident ray and the normal.
Angle 1 is angle of emergence. As, it is formed between the emergent ray with normal.
Angle 4 is angle of refraction. As, it is formed between the refracted ray and the normal.
3 shows the lateral displacement.
Hence, the correct answer is 2, 1, 4, 3
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is atmospheric refraction? Use this phenomenon to explain the following natural events:
Advanced sun-rise and delayed sun-set.
Draw diagrams to illustrate your answers.
The phenomenon that causes the twinkling of stars is refraction of light.
Name two effects produced by the atmospheric refraction.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
We can see the sun about ................ minutes before the actual sunrise and about ................ minutes after the actual sunset because of atmospheric ................
Why do stars seem higher than they actually are? Illustrate your answer with the help of a diagram.
The stars appear higher in the sky than they actually are, due to:
(a) diffraction of light
(b) scattering of light
(c) refraction of light
(d) reflection of light
The stars twinkle but the planets do not twinkle at night because:
(a) the stars are small but the planets are large
(b) the stars are very large but planets are small
(c) the stars are much nearer but planets are far off
(d) the stars are far off but planets are nearer to earth
Which of the following is not caused by the atmospheric refraction of light?
(a) twinkling of stars at night
(b) sun appearing higher in the sky than it actually is
(c) sun becoming visible two minutes before actual sunrise
(d) sun appearing red at sunset
Explain why the planets do not twinkle but the stars twinkle.
Refraction of light by the earth’s atmosphere due to variation in air density is called ____________.
