Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The figure shows a circuit. When the circuit is switched on, the ammeter reads 0.5 A.
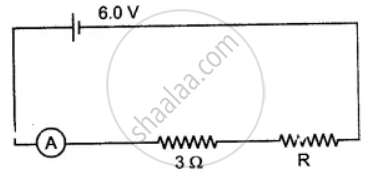
(i) Calculate the value of the unknown resistor R.
(ii) Calculate the charge passing through the 3 Ω resistor in 120 s.
(iii) Calculate the power dissipated in the 3 Ω resistor.
उत्तर
(i) We know, V = IR'
⇒ 6 = 0.5 × R'
⇒ R' = 12 Ohm
∵ R' = 3 + R
⇒ 12 = 3 + R
⇒ R = 9 Ohm
(ii) Charge, q = i t
⇒ q = 0.5 × 120 = 60 Coulomb
(iii) Power dissipation, p = i2R
p = 0.52 × 3 = 0.75 Watt
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following statements correctly defines a volt?
(a) a volt is a joule per ampere.
(b) a volt is a joule per coulomb.
What is the SI unit of potential difference?
How much work is done in moving a charge of 2 C across two points having a potential difference of 12 V?
What is the unit of electric charge?
What p.d. is needed to send a current of 6 A through an electrical appliance having a resistance of 40 Ω?
What is the ratio of potential difference and current known as?
The values of potential difference V applies across a resistor and the corresponding values of current I flowing in the resistor are given below:
| Potential differences, V (in volts) | : | 2.5 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 15.0 | 20.0 | 25.0 |
| Current, I (in amperes) | : | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
A current of 1.6 mA flows through a conductor. If charge on an electron is –1.6 × 10-19 coulomb, find the number of electrons that will pass each second through the cross section of that conductor.
A battery of 10 volt carries 20,000 C of charge through a resistance of 20 Ω. The work done in 10 seconds is:
If P and V are the power and potential of device, the power consumed with a supply potential V1 is:
