Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The figure shows a circuit. When the circuit is switched on, the ammeter reads 0.5 A.
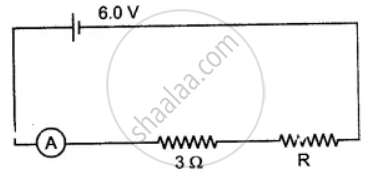
(i) Calculate the value of the unknown resistor R.
(ii) Calculate the charge passing through the 3 Ω resistor in 120 s.
(iii) Calculate the power dissipated in the 3 Ω resistor.
Solution
(i) We know, V = IR'
⇒ 6 = 0.5 × R'
⇒ R' = 12 Ohm
∵ R' = 3 + R
⇒ 12 = 3 + R
⇒ R = 9 Ohm
(ii) Charge, q = i t
⇒ q = 0.5 × 120 = 60 Coulomb
(iii) Power dissipation, p = i2R
p = 0.52 × 3 = 0.75 Watt
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 2 Ω is connected with two resistors A and B of resistance 4 Ω and 6 Ω respectively joined in series.
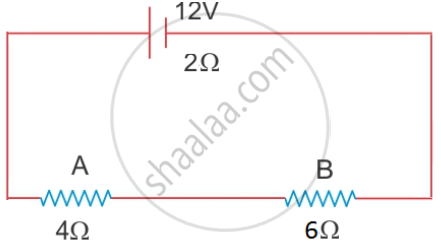
Find:
1) Current in the circuit
2) The terminal voltage of the cell
3) The potential difference across 6Ω Resistor
4) Electrical energy spent per minute in the 4Ω resistor.
Ohm's law state a relation between potential difference and ___________.
What p.d. is needed to send a current of 6 A through an electrical appliance having a resistance of 40 Ω?
The potential difference between the terminals of an electric iron is 240 V and the current is 5.0 A. What is the resistance of the electric iron?
Calculate the potential difference between the two terminals of a battery if 100 joules of work is required to transfer 20 coulombs of charge from one terminal of the battery to the other.
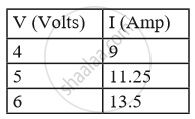
The following table shows current in Amperes and potential difference in Volts.
What will be the nature of the graph between the current and potential difference? (Do not draw a graph.)
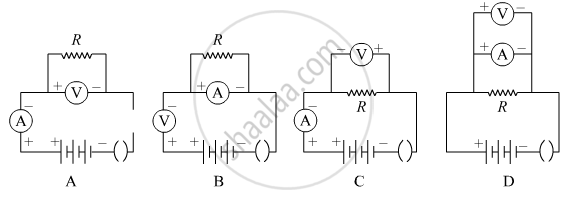
Which one of the following is the correct set-up for studying the dependence of the current on the potential difference across a resistor and why?
Suppose there are three resistors A, B, and C having resistances r1, r2, and r3 respectively. If R represents their equivalent resistance, establish the following relation `1/"R" = 1/"r"_1 + 1/"r"_2 + 1/"r"_3`, when joined in parallel.
A current of 100 mA. flows through a wire. The charge on an electron is 1.6 × 10-19 C. Find the number of electrons passing per second through the cross-section of the conductor.
Potential near a charge is the measure of its ______ to bring a positive charge at that point.
