Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The following question is a case-based question. Read the case carefully and answer the questions that follow.
| The nature of bonding, structure of the coordination compound can be explained to some extent by valence bond theory. The central metal atom/ion makes available a number of vacant orbitals equal to its coordination number. The appropriate atomic orbitals (s, p and d) of the metal hybridise to give a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry such as square planar, tetrahedral, octahedral and so on. A strong covalent bond is formed only when the orbitals overlap to the maximum extent. The d-orbitals involved in the hybridisation may be either inner d-orbitals i.e. (n − 1) d or outer d-orbitals i.e. nd. The complexes formed are called inner orbital complex (low spin complex) and outer orbital complex (high spin complex) respectively. Further, the complexes can be paramagnetic or diamagnetic in nature. The drawbacks of this theory are that this involves number of assumptions and also does not explain the colour of the complex. |
Answer the following questions:
(a) Predict whether \[\ce{[CoF6]^3-}\] is diamagnetic or paramagnetic and why?
[Atomic number: \[\ce{Co}\] = 27] (1)
(b) What is the coordination number of \[\ce{Co}\] in \[\ce{[Co(en)2Cl2]+}\]? (1)
(c) (i) Write the IUPAC name of the given complex: (1)
\[\ce{[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]^2+}\]
(ii) Explain \[\ce{[Co(NH3)6]^3+}\] is an inner orbital or outer orbital complex. (1)
OR
(c) Using valence bond theory, deduce the shape and hybridisation of \[\ce{[Ni(NH3)6]^2+}\] [Atomic number of Ni = 28]. (2)
उत्तर
(a) \[\ce{[CoF6]^3-}\]
\[\ce{Co}\] = 27 = 2, 8, 15, 2
= 1s22s22p63s23p63d74s2
In \[\ce{[CoF6]^3-}\]
x + 6(−1) = −3
x − 6 = −3
x = −3 + 6
x = +3
\[\ce{Co^{+3}}\] means
= 1s22s22p63s23p63d64s04p0
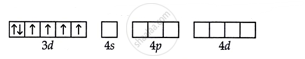
Fluorido is a weak ligand, so it will undergo high spin, sp3d2 hybridisation.
So it will be paramagnetic due to 4 unpaired electrons.
(b) \[\ce{[Co(en)2Cl2]+}\]
⇒ en = ethylenediamine
⇒ It is a bidentate ligand, which means it will provide two lone pairs.
So, cobalt has 2 ethylenediamine
= 2 × 2 + 2 Chlorine
= 4 lone pair + 2 chlorine
= 6
The coordination number is six for cobalt as central metal atom.
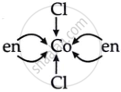
6 is the coordination number.
(c) (i) \[\ce{[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]^2+}\]
x + 2(0) + 2(−1) = +2
x + 0 − 2 = +2
x = +4
IUPAC name: Diamminedichloridoplatinum (IV) ion
(c) (ii) \[\ce{[Co(NH3)6]^3+}\] Since \[\ce{NH3}\] is a barderline ligand it will form an outer orbital complex with sp3d2 hybridisation and is diamagnetic in nature.
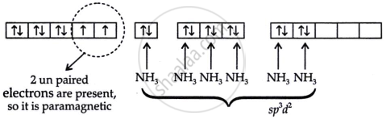
\[\ce{[Ni(NH3)6]^2+}\]
x + 6(0) = +2
x = +2
Thus, \[\ce{Ni^{+2}}\] = 1s22s22p63s23p63d8
OR
(c) The coordination number is six; that means the compound is octahedral in shape.
Since \[\ce{[Ni(NH3)6]^2+}\] is an outer orbital complex it undergoes sp3d2 hybridisation.
