Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2023-2024
Date & Time: 27th February 2024, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS:
Read the following instructions carefully and follow them:
- This question paper contains 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Question paper is divided into FIVE sections - Section A, B, C, D and E.
- Section A - question number 1 to 16 are multiple choice type questions. Each question carries 1 mark.
- Section B - question number 17 to 21 are very short answer type questions. Each question carries 2 marks.
- Section C - question number 22 to 28 are short answer type questions. Each question carries 3 marks.
- Section D - question number 29 and 30 are case-based questions. Each question carries 4 marks.
- Section E - question number 31 to 33 are long answer type questions. Each question carries 5 marks.
- There is no overall choice given in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions in all the Sections except section A.
- Kindly note that there is a separate question paper for Visually Impaired candidates.
- Use of calculator is NOT allowed.
The molar ionic conductivities of \[\ce{Ca^2+}\] and \[\ce{CI-}\] are 119.0 and 76.3 S cm2 mol−1 respectively. The value of limiting molar conductivity of \[\ce{CaCl2}\] will be ______.
195.3 S cm2 mol−1
43.3 S cm2 mol−1
314.3 S cm2 mol−1
271.6 S cm2 mol−1
Chapter:
Consider the following reaction:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{.......}\ce{H}\phantom{..................................}\\
\backslash\phantom{........}\backslash\phantom{...............................}\\
\ce{C = O} + \ce{C = O} + \ce{Conc. KOH ->[\Delta] A +B}\\
/\phantom{........}/\phantom{...............................}\\
\ce{H}\phantom{.......}\ce{H}\phantom{..................................}\\
\end{array}\]
Identify A and B from the given options:
A - Methanol, B - Potassium formate
A - Ethanol, B - Potassium formate
A - Methanal, B - Ethanol
A - Methanol, B - Potassium acetate
Chapter:
Which of the following acids represents Vitamin C?
Saccharic acid
Gluconic acid
Ascorbic acid
Benzoic acid
Chapter:
Rosenmund reduction is used for the preparation of Aldehydes. The catalyst used in this reaction is ______.
\[\ce{Pd - BaSO4}\]
Anhydrous \[\ce{AlCl3}\]
Iron (III) oxide
\[\ce{HgSO4}\]
Chapter:
Which alkyl halide from the given options will undergo SN1 reaction faster?
\[\ce{(CH3)3C - Br}\]
\[\ce{(CH3)2CH - Br}\]
\[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - Br}\]
\[\ce{(CH3)3C - CH2 - Br}\]
Chapter:
From the elements of 3d series given below, which element shows the maximum number of oxidation states?
Scandium
Manganese
Chromium
Titanium
Chapter:
The correct Mathematical expression of Arrhenius equation is ______.
k = −AeEa/RT
k = eEa/RT
k = Ae−Ea/RT
k = −Ae−Ea/RT
Chapter:
Identify the tertiary amine from the following:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{CH3}\\
|\\
\ce{CH3 - N - CH3}
\end{array}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH3}\\
|\phantom{..}\\
\ce{NH}
\end{array}\]
\[\ce{CH3 - NH - CH2 - CH3}\]
\[\ce{(C2H5)2CHNH2}\]
Chapter:
Nucleophilic addition of Grignard reagent to ketones followed by hydrolysis with dilute acids forms ______.
Alkene
Primary alcohol
Tertiary alcohol
Secondary alcohol
Chapter:
In a given graph of zero-order reaction, the slope and intercept are:
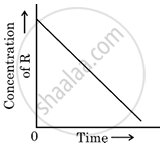
Slope = k, Intercept = [R]0
Slope = −k, Intercept = [R]0
Slope = `k/2.303`, Intercept = In[R]0
Slope = `−k/2.303`, Intercept = In A
Chapter:
Match the reagents required for the given reactions:
| I. | Oxidation of primary alcohols to aldehydes | (p) | \[\ce{NaBH4}\] |
| II. | Butan-2-one to Butan-2-ol | (q) | 85% phosphoric acid at 440 K |
| III. | Bromination of Phenol to 2, 4, 6-Tribromophenol | (r) | PCC |
| IV. | Dehydration of propan-2-ol propene | (s) | Bromine water |
I - (r), II - (p), III - (s), IV - (q)
I - (q), II - (r), III - (p), IV - (s)
I - (s), II - (q), III - (p), IV - (r)
I - (p), II - (s), III - (r), IV - (q)
Chapter:
The general electronic configuration of d-block elements is ______.
(n − 1) d1−10ns1−2
(n − 1) d10ns1−2
(n − 1) d10ns2−3
(n − 1) d0ns1−2
Chapter:
Assertion (A): p-nitrophenol is less acidic than phenol.
Reason (R): Nitro group is electron withdrawing and helps in the stabilisation of p-nitrophenoxide ion.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): Benzoic acid does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Reason (R): Carboxyl group is deactivating and the catalyst aluminium chloride gets bonded to the carboxyl group.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): Fructose is a reducing sugar.
Reason (R): Fructose does not reduce Fehling solution and Tollen’s reagent.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): For a Daniell cell, \[\ce{Zn/Zn^2+(1M) || Cu^2+(1M)/Cu}\] with E0cell = 1.1 V, if the external opposing potential is more than 1.1 V, the electrons flow from \[\ce{Cu to Zn}\].
Reason (R): Cell acts like a galvanic cell.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter:
Define activation energy.
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
18 g of a non-volatile solute is dissolved in 200 g of \[\ce{H2O}\] freezes at 272.07 K. Calculate the molecular mass of solute (Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol−1)
Chapter:
Which compound in the given pair would undergo SN2 reaction at a faster rate and why?
\[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - I and CH3 - CH2 - Br}\]
Chapter:
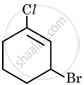
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their boiling points:
Butane, 1-Bromobutane, 1-Iodobutane, 1-Chlorobutane
Chapter:
Write the stepwise mechanism of nucleophilic addition reactions in the carbonyl compounds.
Chapter:
How do you convert the Toluene to Benzoic acid
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Ethanol to 3-Hydroxybutanal
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Advertisements
What happens when glucose reacts with bromine water? Write chemical equation.
Chapter:
Two bases are mentioned below, identify which is present in DNA and which one is present in RNA:
- Thymine,
- Uracil.
Chapter:
Draw the geometrical isomers of complex \[\ce{[Pt(en)2Cl2]^2+}\].
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if ∆0 < P.
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
What is meant by unidentate ligand?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Calculate emf of the following cell at 25°C:
\[\ce{Sn/Sn^2+ (0.001 M) || H+ (0.01 M) | H2_{(g)} (1 bar) | Pt_{(s)}}\]
Given: \[\ce{E^\circ(Sn^2+/sn) = -0.14 V, E^\circ H+/H2 = 0.00 V (log 10 = 1)}\]
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Write chemical equation for the following reaction:
Hydroboration-oxidation reaction
Chapter:
Write chemical equation for the following reaction:
Williamson Synthesis
Chapter:
Write chemical equation for the following reaction:
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation of Anisole
Chapter:
Write the equation involved in the following reaction:
Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write chemical test to distinguish between the following compounds:
Phenol and Benzoic acid
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Propanal and Propanone
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Which one of the given compounds is a stronger acid and why?
\[\ce{CH2FCH2CH2COOH or CH3CHFCH2COOH}\]
Chapter:
Explain the following term:
Essential amino acids
Chapter:
The presence of \[\ce{-NO2}\] group at ortho or para position increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions. Give reason to explain the above statement.
Chapter:
What happens when ethyl chloride is treated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide?
Chapter:
Show that the time required for 99.9% completion in a first order reaction is 10 times of half-life (t1/2) of the reaction [log 2 = 0.3010, log 10 = 1].
Chapter:
The following question is a case-based question. Read the case carefully and answer the questions that follow.
| The nature of bonding, structure of the coordination compound can be explained to some extent by valence bond theory. The central metal atom/ion makes available a number of vacant orbitals equal to its coordination number. The appropriate atomic orbitals (s, p and d) of the metal hybridise to give a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry such as square planar, tetrahedral, octahedral and so on. A strong covalent bond is formed only when the orbitals overlap to the maximum extent. The d-orbitals involved in the hybridisation may be either inner d-orbitals i.e. (n − 1) d or outer d-orbitals i.e. nd. The complexes formed are called inner orbital complex (low spin complex) and outer orbital complex (high spin complex) respectively. Further, the complexes can be paramagnetic or diamagnetic in nature. The drawbacks of this theory are that this involves number of assumptions and also does not explain the colour of the complex. |
Answer the following questions:
(a) Predict whether \[\ce{[CoF6]^3-}\] is diamagnetic or paramagnetic and why?
[Atomic number: \[\ce{Co}\] = 27] (1)
(b) What is the coordination number of \[\ce{Co}\] in \[\ce{[Co(en)2Cl2]+}\]? (1)
(c) (i) Write the IUPAC name of the given complex: (1)
\[\ce{[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]^2+}\]
(ii) Explain \[\ce{[Co(NH3)6]^3+}\] is an inner orbital or outer orbital complex. (1)
OR
(c) Using valence bond theory, deduce the shape and hybridisation of \[\ce{[Ni(NH3)6]^2+}\] [Atomic number of Ni = 28]. (2)
Chapter:
Advertisements
The following question is a case-based question. Read the case carefully and answer the questions that follow.
|
In a galvanic cell, chemical energy of a redox reaction is converted into electrical energy, whereas in an electrolytic cell the redox reaction occurs on passing electricity. The simplest galvanic cell is in which \[\ce{Zn}\] rod is placed in a solution of \[\ce{ZnSO4}\] and \[\ce{Cu}\] rod is placed in a solution of \[\ce{CuSO4}\]. The two rods are connected by a metallic wire through a voltmeter. The two solutions are joined by a salt bridge. The difference between the two electrode potentials of the two electrodes is known as electromotive force. In the process of electrolysis, the decomposition of a substance takes place by passing an electric current. One mole of electric charge when passed through a cell will discharge half a mole of a divalent metal ion such as \[\ce{Cu^2+}\]. This was first formulated by Faraday in the form of laws of electrolysis. |
Answer the following questions:
(a) What is the function of a salt bridge in a galvanic cell? (1)
(b) When does galvanic cell behave like an electrolytic cell? (1)
(c) Can copper sulphate solution be stored in a pot made of zinc? Explain with the help of the value of \[\ce{E^0_{cell}}\]. (2)
\[\ce{(E^0 Cu^2+/Cu = 0.34V)}\]
\[\ce{(E^0 Zn^2+/Zn = -0.76V)}\]
OR
(c) How much charge in terms of Faraday is required for the following: (2)
- 1 mol of \[\ce{MnO^-4}\] to \[\ce{Mn^2+}\]
- 1 mol of \[\ce{H2O}\] to \[\ce{O2}\]
Chapter:
Why Zinc is not regarded as a transition element?
Chapter:
What is Lanthanoid contraction?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Why first ionization enthalpy of chromium is lower than that of zinc?
Chapter:
Give reasons for the following:
The transition metals generally form coloured compounds.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Out of \[\ce{KMnO4}\] and \[\ce{K2MnO4}\], which one is paramagnetic and why?
Chapter:
Complete the following ionic equation:
\[\ce{Cr2O^2-_7 + 14H+ + 6e- ->}\]
Chapter:
Why are aquatic species more comfortable in cold water in comparison to warm water?
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
A solution containing 2 g of glucose (M = 180 g mol−1) in 100 g of water is prepared at 303 K. If the vapour pressure of pure water at 303 K is 32.8 mm Hg, what would be the vapour pressure of the solution?
Chapter:
Predict whether Van't Hoff factor will be less or greater than one, when Ethanoic acid is dissolved in benzene.
Chapter:
Define the term:
Ideal solution
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Calculate the mass of \[\ce{CaCl2}\] (molar mass = 111 g mol−1) to be dissolved in 500 g of water to lower its freezing point by 2K, assuming that \[\ce{CaCl2}\] undergoes complete dissociation.
(Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol−1)
Chapter:
An amide ‘A’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H7ON}\] undergoes Hoffmann Bromamide degradation reaction to give amine ‘B’. 'B’ on treatment with nitrous acid at 273-278 K form ‘C’ and on treatment with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide forms 'D’. ‘C’ on treatment, with ethanol gives ‘E’. Identify ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’ ‘D’ and ‘E' and write the sequence of chemical equations.
Chapter:
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their basic strength in gaseous phase:
\[\ce{C2H5NH2, (C2H5)3N, (C2H5)2NH}\]
Chapter:
Give reason for the following:
Methyl amine is more basic than aniline.
Chapter:
Give reason for the following:
Aniline readily reacts with bromine water to give 2, 4, 6-tribromoaniline.
Chapter:
Give reason for the following:
Primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry with solutions 2023 - 2024
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2024 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.