Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is −13.6 eV. What are the kinetic and potential energies of the electron in this state?
उत्तर
Ground state energy of hydrogen atom, E = − 13.6 eV
This is the total energy of a hydrogen atom. Kinetic energy is equal to the negative of the total energy.
Kinetic energy = − E = − (− 13.6) = 13.6 eV
Potential energy is equal to the negative of two times of kinetic energy.
Potential energy = − 2 × (13.6) = − 27.2 eV
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given the ground state energy E0 = - 13.6 eV and Bohr radius a0 = 0.53 Å. Find out how the de Broglie wavelength associated with the electron orbiting in the ground state would change when it jumps into the first excited state.
A 12.5 eV electron beam is used to bombard gaseous hydrogen at room temperature. Upto which energy level the hydrogen atoms would be excited? Calculate the wavelengths of the first member of Lyman and first member of Balmer series.
A difference of 2.3 eV separates two energy levels in an atom. What is the frequency of radiation emitted when the atom makes a transition from the upper level to the lower level?
A hydrogen atom initially in the ground level absorbs a photon, which excites it to the n = 4 level. Determine the wavelength and frequency of the photon.
The total energy of an electron in the first excited state of the hydrogen atom is about −3.4 eV.
What is the potential energy of the electron in this state?
The total energy of an electron in the first excited state of the hydrogen atom is about −3.4 eV.
Which of the answers above would change if the choice of the zero of potential energy is changed?
Obtain the first Bohr’s radius and the ground state energy of a muonic hydrogen atom [i.e., an atom in which a negatively charged muon (μ−) of mass about 207 me orbits around a proton].
A 12.3 eV electron beam is used to bombard gaseous hydrogen at room temperature. Upto which energy level the hydrogen atoms would be excited?
Calculate the wavelengths of the second member of Lyman series and second member of Balmer series.
Draw the energy level diagram showing how the line spectra corresponding to Paschen series occur due to transition between energy levels.
Calculate the minimum amount of energy which a gamma ray photon should have for the production of an electron and a positron pair..
A Carnot engine absorbs 1000 J of heat energy from a reservoir at 127°C and rejects 600 J of heat energy during each cycle. The efficiency of the engine and temperature of the sink will be:
The Ionisation energy of hydrogen atom is 3.6 ev The ionisation energy of helium atom would be
Energy of an electron at infinity from nucleus is ______.
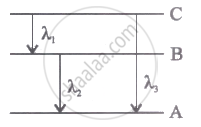
Energy levels A, B, C of acertain atom corresponding to increasing value of energy, i.e., EA< E8 < Ee. If λ1, λ2 and λ3 are the wavelength of radiations corresponding to the transitions C to B, B to A and C to A respectively, which of the following statements is correct?
Radiation coming from transitions n = 2 to n = 1 of hydrogen atoms fall on He+ ions in n = 1 and n = 2 states. The possible transition of helium ions as they absorb energy from the radiation is ______.
Which of the following is true for X-rays?
