Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The line 2x + 3y = 12 touches the ellipse `x^2/9 + y^2/4` = 2 at the point (3, 2).
पर्याय
True
False
उत्तर
This statement is True.
Explanation:
If line 2x + 3y = 12 touches the ellipse `x^2/9 + y^2/4` = 2
Then the point (3, 2) satisfies both line and ellipse.
∴ For line 2x + 3y = 12
2(3) + 3(2) = 12
6 + 6 = 12
12 = 12
For ellipse `x^2/9 + y^2/4` = 2
`(3)^2/9 + (2)^2/4` = 2
`9/9 + 4/4` = 2
1 + 1 = 2
2 = 2
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the equation for the ellipse that satisfies the given condition:
Vertices (±5, 0), foci (±4, 0)
Find the equation for the ellipse that satisfies the given conditions:
Vertices (0, ±13), foci (0, ±5)
Find the equation for the ellipse that satisfies the given conditions:
Length of major axis 26, foci (±5, 0)
Find the equation for the ellipse that satisfies the given conditions:
Length of minor axis 16, foci (0, ±6)
Find the equation for the ellipse that satisfies the given conditions:
Foci (±3, 0), a = 4
Find the equation for the ellipse that satisfies the given conditions:
Centre at (0, 0), major axis on the y-axis and passes through the points (3, 2) and (1, 6)
Find the equation for the ellipse that satisfies the given conditions:
Major axis on the x-axis and passes through the points (4, 3) and (6, 2).
Find the equation of the ellipse in the case:
focus is (0, 1), directrix is x + y = 0 and e = \[\frac{1}{2}\] .
Find the equation of the ellipse in the case:
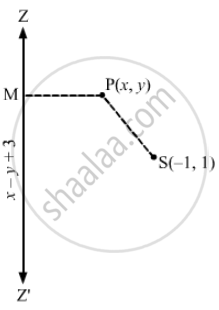
focus is (−1, 1), directrix is x − y + 3 = 0 and e = \[\frac{1}{2}\]
Find the equation of the ellipse in the case:
focus is (1, 2), directrix is 3x + 4y − 5 = 0 and e = \[\frac{1}{2}\]
Find the equation to the ellipse (referred to its axes as the axes of x and y respectively) which passes through the point (−3, 1) and has eccentricity \[\sqrt{\frac{2}{5}}\]
Find the equation of the ellipse in the case:
eccentricity e = \[\frac{1}{2}\] and foci (± 2, 0)
Find the equation of the ellipse in the case:
eccentricity e = \[\frac{2}{3}\] and length of latus rectum = 5
Find the equation of the ellipse in the case:
Vertices (± 5, 0), foci (± 4, 0)
Find the equation of the ellipse in the following case:
Vertices (± 6, 0), foci (± 4, 0)
Find the equation of the ellipse in the following case:
Ends of major axis (± 3, 0), ends of minor axis (0, ± 2)
Find the equation of the ellipse in the following case:
Ends of major axis (0, ±\[\sqrt{5}\] ends of minor axis (± 1, 0)
Find the equation of the ellipse in the following case:
Length of major axis 26, foci (± 5, 0)
Find the equation of the ellipse in the following case:
Length of minor axis 16 foci (0, ± 6)
Find the equation of the ellipse in the following case:
Foci (± 3, 0), a = 4
Find the equation of ellipse whose eccentricity is `2/3`, latus rectum is 5 and the centre is (0, 0).
If P is a point on the ellipse `x^2/16 + y^2/25` = 1 whose foci are S and S′, then PS + PS′ = 8.
An ellipse is described by using an endless string which is passed over two pins. If the axes are 6 cm and 4 cm, the length of the string and distance between the pins are ______.
The equation of the ellipse having foci (0, 1), (0, –1) and minor axis of length 1 is ______.
