Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The potential difference between the terminals of a battery of emf 6.0 V and internal resistance 1 Ω drops to 5.8 V when connected across an external resistor. Find the resistance of the external resistor.
उत्तर
Given:-
Emf of the battery, E = 6 V
Internal resistance, r = 1 Ω
Potential difference, V = 5.8 V
Let R be the resistance of the external resistor.
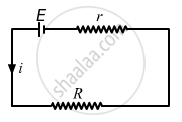
Applying KVL in the above circuit, we get:-
\[E - i(R + r) = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow i = \frac{E}{R + r}\]
\[ = \frac{6}{R + 1}\]
Also,
\[V = E - ir\]
\[ \Rightarrow 5 . 8 = 6 - \frac{6}{R + 1} \times 1\]
\[\frac{6}{R + 1} = 0 . 2\]
\[R + 1 = \frac{6}{0 . 2} = 30\]
\[R = 29 \Omega\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a series LCR circuit, what is the phase difference between VL and VC where VL is the potential difference across the inductor and V c is the potential difference across the capacitor?
Describe the working principle of a solar cell. Mention three basic processes involved in the generation of emf.
Why are Si and GaAs preferred materials for solar cells?
Identify the correct options.
(a) An ammeter should have small resistance.
(b) An ammeter should have large resistance.
(c) A voltmeter should have small resistance.
(d) A voltmeter should have large resistance.
The current in a conductor and the potential difference across its ends are measured by an ammeter and a voltmeter. The meters draw negligible currents. The ammeter is accurate but the voltmeter has a zero error (that is, it does not read zero when no potential difference is applied). Calculate the zero error if the readings for two different conditions are 1.75 A, 14.4 V and 2.75 A, 22.4 V.
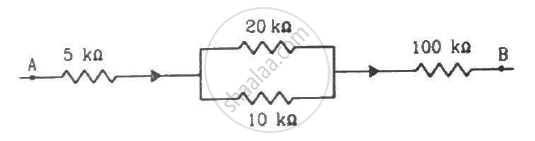
The following figure shows a part of a circuit. If a current of 12 mA exists in the 5 kΩ resistor, find the currents in the other three resistors. What is the potential difference between the points A and B?
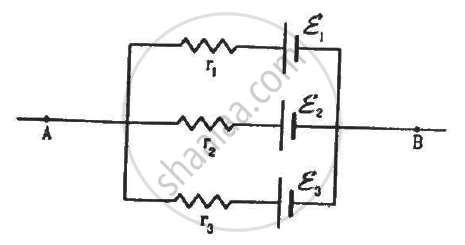
Find the potential difference Va – Vb in the circuits shown in the figure.
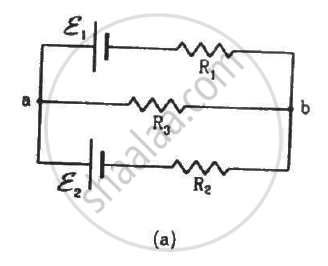
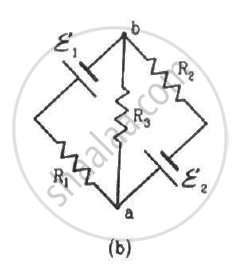
In the circuit shown in the figure, ε1 = 3 V, ε2 = 2 V, εa = 1 V and r1 = r2 = r3 = 1Ω. Find the potential difference between the points A and B and the current through each branch.
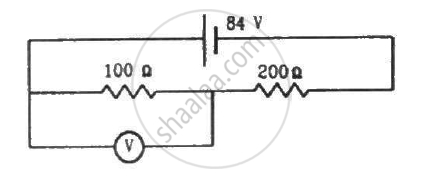
A voltmeter of resistance 400 Ω is used to measure the potential difference across the 100 Ω resistor in the circuit shown in the figure. (a) What will be the reading of the voltmeter? (b) What was the potential difference across 100 Ω before the voltmeter was connected?
A voltmeter consists of a 25 Ω coil connected in series with a 575 Ω resistor. The coil takes 10 mA for full-scale deflection. What maximum potential difference can be measured by this voltmeter?
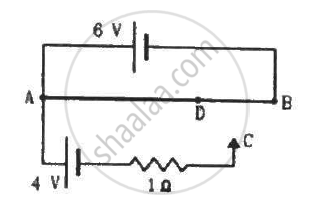
A 6-volt battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a uniform wire AB of length 100 cm. The positive terminal of another battery of emf 4 V and internal resistance 1 Ω is joined to the point A, as shown in the figure. Take the potential at B to be zero. (a) What are the potentials at the points A and C? (b) At which point D of the wire AB, the potential is equal to the potential at C? (c) If the points C and D are connected by a wire, what will be the current through it? (d) If the 4 V battery is replaced by a 7.5 V battery, what would be the answers of parts (a) and (b)?
The potential difference across the terminals of a battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 2 Ω drops to 10 V when it is connected to a silver voltameter. Find the silver deposited at the cathode in half an hour. Atomic weight of silver is 107.9 g mol−1.
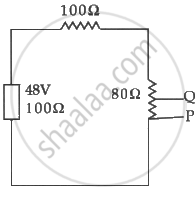
In the circuit in figure the potential difference across P and Q will be nearest to