Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 3/2. What is the refractive index of air with respect to glass?
उत्तर
Given: aμg = `3/2`
gμa = `1/(""_"a"mu_"g")`
= `1/(3//2)`
= `2/3`
= 0.67.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the adjacent diagram, AO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab.
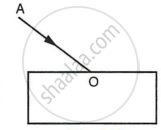
- Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out of the slab.
- In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
- Mark angles of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
- Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
- Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray. State one factor that affects the lateral displacement.
What do you understand by the statement the refractive index of glass is 1.5 for white light?
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is expressed as `""_g μ_a=sin i /sin r`.
- Write down a similar expression for aμg in terms of the angles i and r.
- If angle r = 90°, what is the corresponding angle i called?
- What is the physical significance of the angle i in part (b)?
Rahim recorded the following sets of observations while tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence.
|
S. No. |
Angle of incidence |
Angle of refraction |
Angle of emergence |
|
I |
45° |
41° |
45° |
|
II |
40° |
38° |
38° |
|
III |
45° |
41° |
40° |
|
IV |
41° |
45° |
41° |
The correct observation is recorded at serial number:
(1) I
(2) II
(3) III
(4) IV
In an experiment of finding the refractive index of glass, if blue light is replaced by the red light, how will the refractive index of glass change? Give reason in support of your answer.
A coin placed at the bottom of a beaker appears to be raised by 4.0 cm. If the refractive index of water is 4/3, find the depth of the water in the beaker.
A ray of light is incident at an angle of 45° on one face of a rectangular glass slab of thickness 10 cm and refractive index 3/2. Calculate the lateral shift produced ______.
The diagram below shows two parallel rays A (Orange) & B (Blue) incident from air, on air-glass boundary.
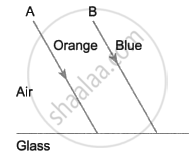
- Copy and complete the path of the rays A and B.
- How do the speeds of these rays differ in glass?
- Are the two refracted rays in glass parallel? Give a reason.
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence in air is
- 0°,
- 45°.
In each case, draw a diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
