Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the approximate values of speed of light in (i) air and (ii) glass. Use these values to calculate the refractive index of glass with respect to air.
उत्तर
(i) Speed of light in air = 3 × 108 ms-1
(ii) Speed of light in glass = 2 × 108 ms-1
Refractive index of glass with respect to air
= `"Speed of light in air"/"Speed of light in glass"`
= `(3xx10^8)/(2xx10^8)`
= `3/2`
= 1.5
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The speed of light in glass is 2 × 105 km/s. What is the refractive index of glass?
Observe the following figure and answer the questions given under it:
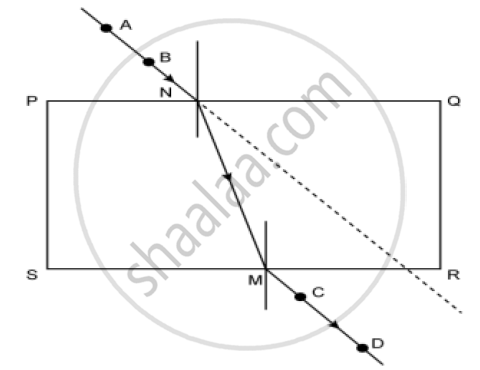
1) How many times does refraction take place in the above figure?
2) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from air to glass?
3) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from glass to air?
4) What are the rays AB and CD in the figure called?
5) Define refraction.
How is the refractive index of a medium related to the speed of light in it?
In the adjacent diagram, AO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab.
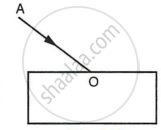
- Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out of the slab.
- In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
- Mark angles of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
- Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
- Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray. State one factor that affects the lateral displacement.
A light ray in passing from water to a medium
(a) speeds up
(b) slows down. In each case, give one example of the medium.
Which of the following is the best experimental set-up out of the four shown for tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab ?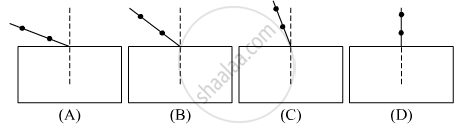
A ray of light falls normally on the surface of a transparent glass slab. Draw a ray diagram to show its path and also mark angle of incidence and angle of emergence.
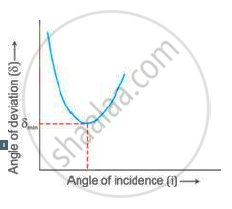
Using the curve, how do you infer that for given prism, the angle of minimum deviation δmin is unique for the given light?
A total reflecting equilateral prism can be used to deviate a ray of light through:
Does the depth of a tank of water appear to change or remain the same when viewed normally from above?
