Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The value of the universal gas constant depends upon
पर्याय
Temperature of the gas
Volume of the gas
Number of moles of the gas
Units of pressure and volume
उत्तर
Units of pressure and volume
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Calculate the volume occupied by 8.8 g of CO2 at 31.1°C and 1 bar pressure. R = 0.083 bar L K–1 mol–1.
Which of the following is the correct expression for the equation of state of van der Waals gas?
Which of the following diagrams correctly describes the behaviour of a fixed mass of an ideal gas? (T is measured in K)
Explain whether a gas approaches ideal behavior or deviates from ideal behaviour if it is compressed to a smaller volume at a constant temperature.
Explain whether a gas approaches ideal behavior or deviates from ideal behaviour if the temperature is raised while keeping the volume constant.
Which of the following gases would you expect to deviate from ideal behavior under conditions of low-temperature F2, Cl2, or Br2? Explain.
Under which of the following two conditions applied together, a gas deviates most from the ideal behaviour?
(i) Low pressure
(ii) High pressure
(iii) Low temperature
(iv) High temperature
Compressibility factor, Z, of a gas is given as Z = `(pV)/(nRT)`. For real gas what will be the effect on value of Z above Boyle’s temperature?
Match the following graphs of ideal gas with their co-ordinates:
| Graphical representation | x and y co-ordinates |
(i)  |
(a) pV vs. V |
(ii) 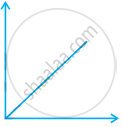 |
(b) p vs. V |
(iii) 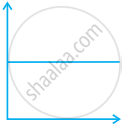 |
(c) p vs. `1/V` |
Assertion (A): At constant temperature, pV vs V plot for real gases is not a straight line.
Reason (R): At high pressure all gases have \[\ce{Z}\] > 1 but at intermediate pressure most gases have \[\ce{Z}\] < 1.
