Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
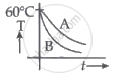
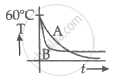
Two identical beakers A and B contain equal volumes of two different liquids at 60°C each and is left to cool down. Liquid in A has a density of 8 × 102 kg/m3 and specific heat of 2000 J kg-1 K-1 while the liquid in B has a density of 103 kg m-3 and specific heat of 4000 J kg-1 K-1. Which of the following best describes their temperature versus time graph schematically? (assume the emissivity of both the beakers to be the same.)
पर्याय
उत्तर
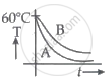
Explanation:
Given: T = 60°C is the initial temperature of both beakers A and B.
The liquid volume in both beakers is the same,
V = VA = VB
The liquid density in beaker A is
ρA = 8 × 102 kg/m3
The liquid density in beaker B is
ρB = 103 kg/m3,
Beaker A's liquid-specific heat is
SA = 2000 J kg-1 k-1,
Beaker B's liquid-specific heat is
SB = `4000J/(kg.K)`
To find: Select the appropriate cooling graph for both liquids.
Cooling law of Newton:
`(dQ)/(dt) = h/(ms)(T - T_0)`
= `h/(Vrhos)(T - T_0)`
In the equation above, `(dQ)/(dt)` stands for the rate of cooling, h for the heat transfer coefficient, m = Vρ for the mass of the liquid, s for its specific heat, T for its temperature, T0 for its environment, V for volume, and ρ for its density.
h, V, T, and T0 are constants for both liquids in beakers A and B:
`(dQ_A)/(dt) ∝ 1/(rho_AS_A); (dQ_B)/(dt) ∝ 1/(rho_sS_B)` .......(i)
Add the supplied values to the equation (i),
`(dQ_A)/(dt) ∝ 1/(800 xx 2000);`
`(dQ_A)/(dt) ∝ 6.25 xx 10^-7` .....(ii)
As shown by equations (ii) and (iii),
`(dQ_A)/(dt) > (dQ_B)/(dt)`
for the duration of cooling.
Hence, as illustrated in option b, graph B will always be above graph A.