Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two long straight parallel conductors carrying steady currents I1 and I2 are separated by a distance 'd'. Explain briefly, with the help of a suitable diagram, how the magnetic field due to one conductor acts on the other. Hence deduce the expression for the force acting between the two conductors. Mention the nature of this force.
उत्तर
Assumption: Current flows in the same direction.
Using Right hand thumb rule, the direction of the magnetic field at point P due to current I2 is perpendicular to the plane of paper and inwards.
Similarly, at point Q on X2Y2, the direction of magnetic field due to current I1 is perpendicularly outward.
Using Fleming’s left hand rule we can find the direction of forces F12 and F21 which are in opposite directions thus,
By Ampere’s circuited law, we have,

`B^2 =mu_0/(4pi) (2I_2)/d`
Now, F12 = I1LB2 (Where L ≡ length of the conductors)
`F_12 =(mu_0)/(4pi) (2I_1I_2L)/d =mu_0/(2pi)(I_1I_2L)/d`
In similar manner we get,
`F_21 =mu_0/(2pi) (I_1I_2L)/d .... (1)`
From above we get the magnitude of forces F12 and F21 are equal but in opposite direction. So,
F12 = −F21
Therefore, two parallel straight conductors carrying current in the same direction attract each other.
Similarly, we can prove if two parallel straight conductors carry currents in opposite direction, they repel each other with the same magnitude as equation (1).
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show with the help of a diagram how the force between the two conductors would change when the currents in them flow in the opposite directions?
The motion of copper plate is damped when it is allowed to oscillate between the two poles of a magnet. What is the cause of this damping?
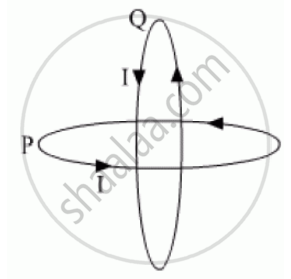
Two identical circular wires P and Q each of radius R and carrying current ‘I’ are kept in perpendicular planes such that they have a common centre as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at the common centre of the two coils.
A moving charge produces
A charged particle moves through a magnetic field perpendicular to its direction. Then ______.
If an electron is moving with velocity `vecnu` produces a magnetic field `vec"B"`, then ______.
A charged particle moving in a magnetic field experiences a resultant force ______
An α particle is moving along a circle of radius R with a constant angular velocity ω. Point A lies in the same plane at a distance 2R from the centre. Point A records magnetic field produced by α particle, if the minimum time interval between two successive times at which A records zero magnetic field is 't' the angular speed ω, in terms of t is ______.
Protons and singly ionized atoms of U235 and U238 are passed in turn (which means one after the other and not at the same time) through a velocity selector and then enter a uniform magnetic field. The protons describe semicircles of radius 10 mm. The separation between the ions of U235 and U238 after describing the semicircle is given by ______.
