Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two opposite angles of a parallelogram are 100° each. Find each of the other two opposite angles.
उत्तर
Given: Two opposite angles of a parallelogram are 100° each.
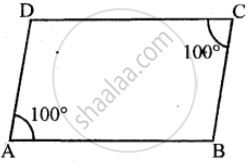
∵ Adjacent angles of a parallelogram are supplementary,
∴ ∠A + ∠B = 180°
⇒ 100° + ∠B = 180°
⇒ ∠B = 180° – 100°
⇒ ∠B = 80°
Also, opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal
∴∠D = ∠B = 80°
∴∠B = ∠D = 80°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The perimeter of a parallelogram is 22 cm . If the longer side measures 6.5 cm what is the measure of the shorter side?
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Vertices .
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The number of pairs of adjacent angles of a quadrilateral is .......
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A diagonal of a quadrilateral is a line segment that joins two ...... vertices of the quadrilateral.
In Fig. 16.19, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
How many pairs of opposite sides are there?
The four angles of a quadrilateral are as 3 : 5 : 7 : 9. Find the angles.
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
The opposite sides of a quadrilateral have
From the following figure find;
- x
- ∠ABC
- ∠ACD
In a trapezium ABCD, side AB is parallel to side DC. If ∠A = x° and ∠D = (3x – 20)°; find the value of x.
Find the angles of a pentagon which are in the ratio 4: 4: 6: 7: 6.
Calculate the measure of each angle of a nonagon.
In the quadrilateral ABCD, AB = BC and AD = DC Measure of ∠BCD is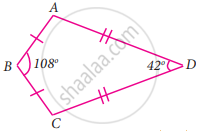
What is the maximum number of obtuse angles that a quadrilateral can have?
Both the pairs of opposite angles of a quadrilateral are equal and supplementary. Find the measure of each angle.
In figure, if point A is shifted to point B along the ray PX such that PB = 2PA, then the measure of ∠BPY is ______.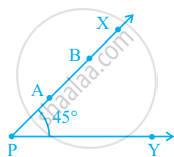
The number of straight angles in figure is ______.
The number of right angles in a straight angle is ______ and that in a complete angle is ______.
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
RT ⊥ ST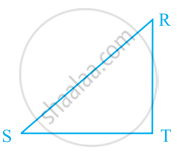
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
RS ⊥ RW
Can we have two obtuse angles whose sum is a complete angle? Why or why not?
