Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Both the pairs of opposite angles of a quadrilateral are equal and supplementary. Find the measure of each angle.
उत्तर
Let ABCD be a quadrilateral.
So, ∠A = ∠C
∠B = ∠D
And ∠A + ∠C = 180°, ∠B + ∠D = 180°
Now, ∠A + ∠A = 180° ...[∠C = ∠A]
⇒ 2∠A = 180°
⇒ ∠A = 90°
Similarly, ∠B = 90°
Hence, each angle is a right angle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a quadrilateral ABCD, CO and DO are the bisectors of ∠C and ∠D respectively. Prove that \[∠COD = \frac{1}{2}(∠A + ∠B) .\]
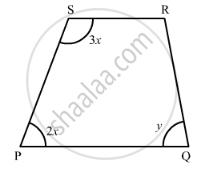
In the given figure, PQRS is an isosceles trapezium. Find x and y.
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If opposite angles of a quadrilateral are equal, then it is necessarily a ....................
Two angles of a quadrilateral are 89° and 113°. If the other two angles are equal; find the equal angles.
The three angles of a quadrilateral are 71°, 110°, 95°. Find its fourth angle.
Find the angles of a quadrilateral whose angles are in the ratio 1: 4: 5: 2.
The angles of a pentagon are x°, (x - 10)°, (x + 20)°, (2x - 44)° and (2x - 70)°. Find the angles.
What is the maximum number of obtuse angles that a quadrilateral can have?
The number of obtuse angles in figure is ______.
If the sum of two angles is equal to an obtuse angle, then which of the following is not possible?
